Netty netty官网: https://netty.io/
什么是Netty?
Netty 是 一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端。
Netty 是一个 NIO 客户端服务器框架,可以快速轻松地开发网络应用程序(例如协议服务器和客户端)。它极大地简化了 TCP 和 UDP 套接字服务器等网络编程。
Java IO 什么是Java IO? 官方文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/io/
I/O(Input/Output) 是计算机与外部设备(磁盘、网络、键盘等)进行数据交换的过程
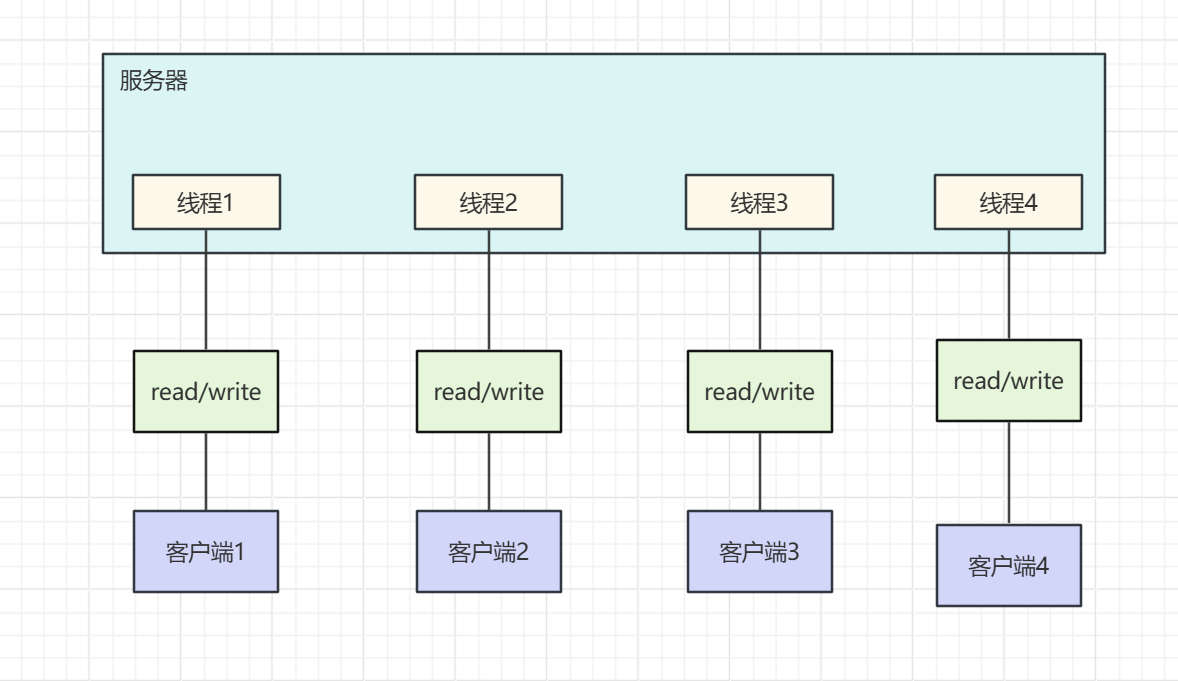
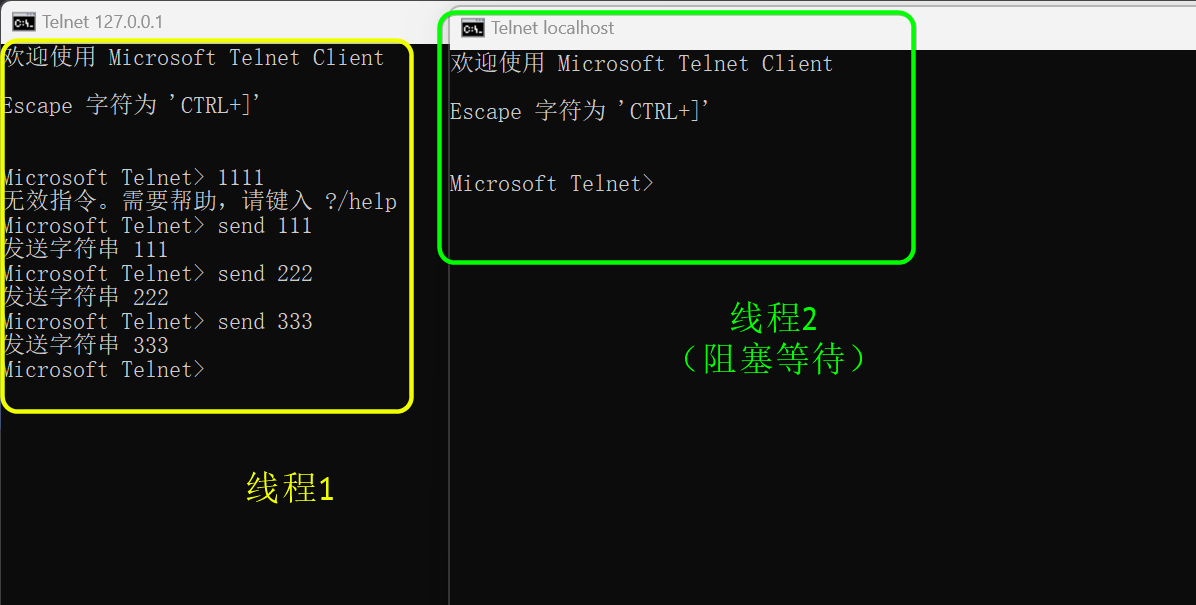
分类 1.BIO (阻塞IO) 每当有一个客户端与服务器进行连接,服务器就会创建一个线程去处理当前连接,当通道没有数据的时候,线程会阻塞等待
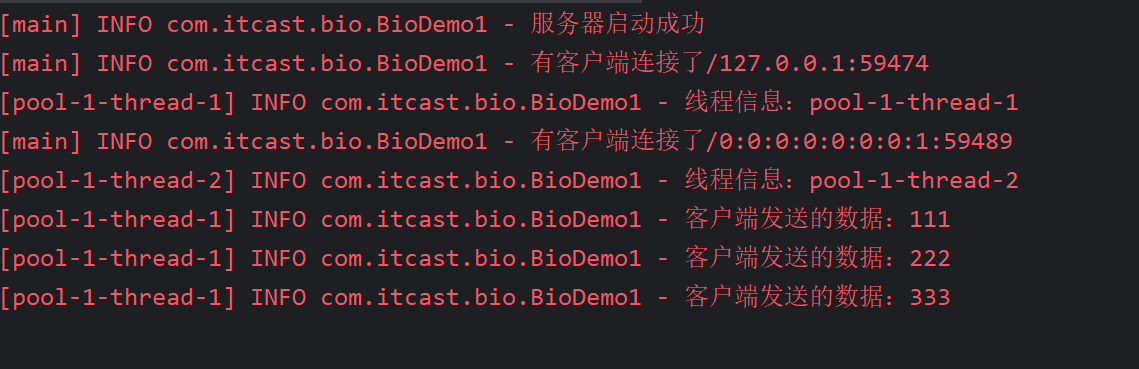
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 @Slf4j public class BioDemo1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ServerSocket socketServer = new ServerSocket (3333 ); log.info("服务器启动成功" ); while (true ) { Socket socket = socketServer.accept(); log.info("有客户端连接了" + socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()); executorService.execute(() -> { try { handle(socket); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } } private static void handle (Socket socket) throws IOException { if (socket.isClosed()) return ; log.info("线程信息:{}" , Thread.currentThread().getName()); InputStream inputStream = null ; try { inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 ]; while (true ) { int read = inputStream.read(bytes); if (read == -1 ) break ; log.info("客户端发送的数据:{}" , new String (bytes, 0 , read)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { log.info("客户端断开连接" + socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()); if (inputStream != null ) inputStream.close(); socket.close(); } } }
文件传输
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class FileDemoServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File ("file/test01.txt" ); RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile (file, "rw" ); byte [] bytes = new byte [(int ) file.length()]; randomAccessFile.read(bytes); ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket (3333 ); Socket client = server.accept(); OutputStream outputStream = client.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write(bytes); outputStream.close(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class FileDemoClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket (); socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 ]; inputStream.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String (bytes)); } }
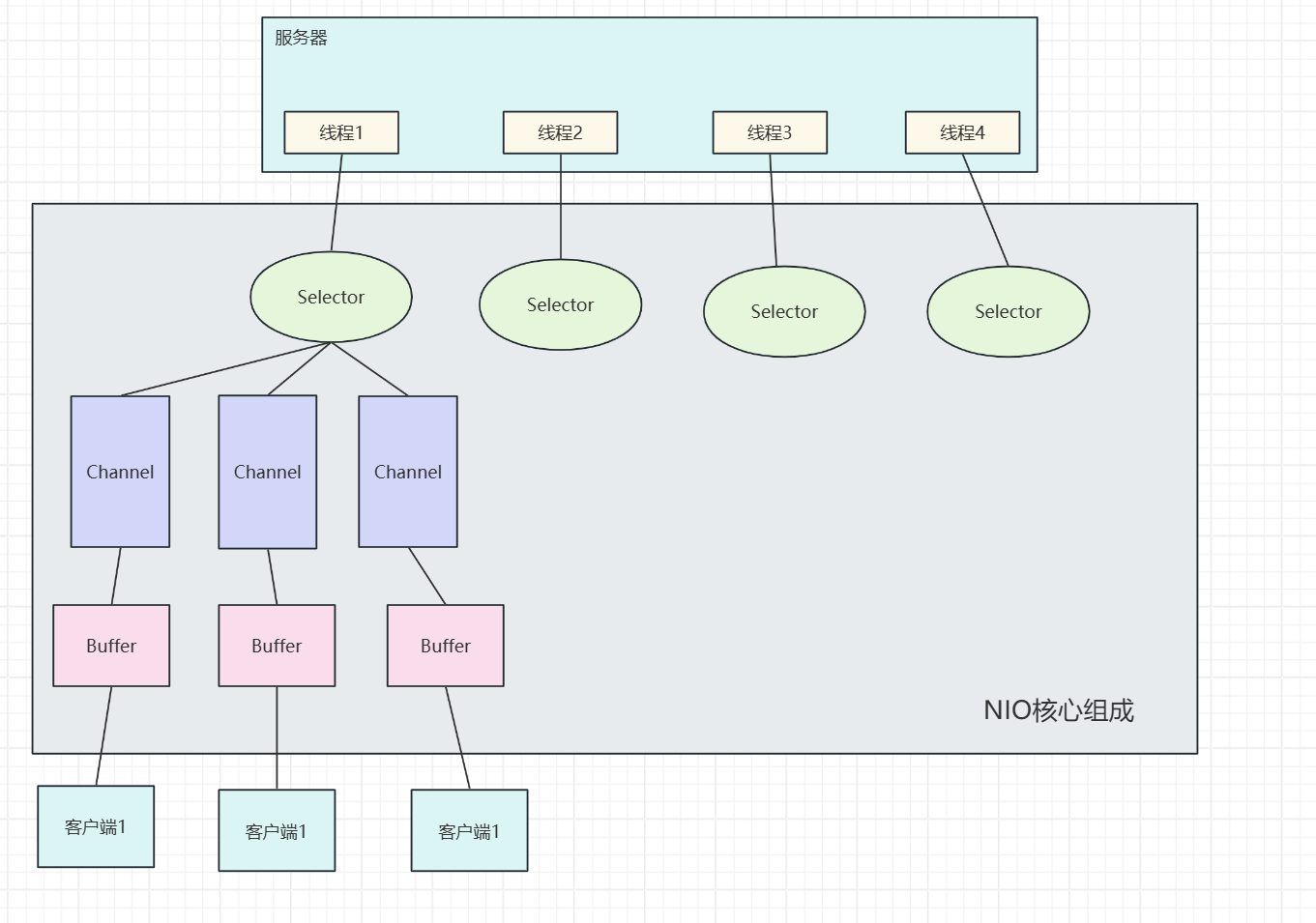
2.NIO (非阻塞IO) 官方文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/package-summary.html
NIO是面向缓冲区或者面向块编程的
核心组成是Selector、Channel、Buffer
1.Channel(通道)
作用 :双向数据传输管道(支持读和写),替代传统 BIO 的流(Stream)。类型 :
SocketChannel:TCP 客户端通道。ServerSocketChannel:TCP 服务端监听通道。FileChannel:文件读写通道。
2. Buffer(缓冲区) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private int mark = -1 ;private int position = 0 ;private int limit;private int capacity;
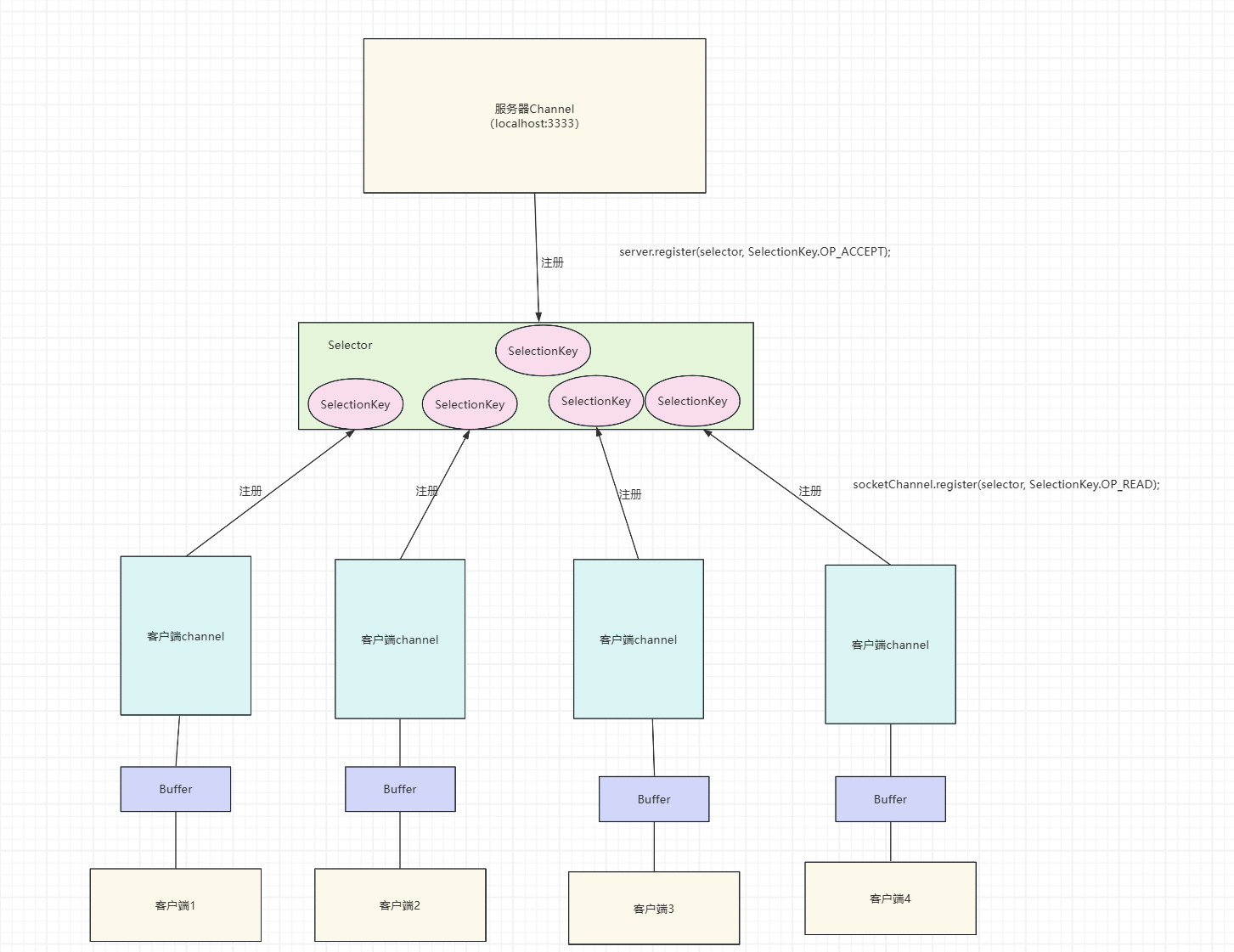
3. Selector(选择器)
作用 :单线程监听多个通道的 I/O 事件(如连接、读、写),实现多路复用。核心事件 :
OP_ACCEPT:服务端接收新连接。OP_CONNECT:客户端完成连接。OP_READ:数据可读。OP_WRITE:数据可写。
3. I/O 多路复用
特点 :通过 Selector/Epoll 监控多个 I/O 事件,当某个通道就绪时通知线程处理。优点 :单线程高效管理多个连接,减少线程切换开销。核心组件 :
Selector(Java NIO)epoll(Linux)kqueue(BSD)
应用场景 :高并发服务器(如 Netty、Nginx)。
4.AIO 异步 I/O(Asynchronous I/O,AIO)
特点 :线程发起 I/O 操作后立即返回,内核负责将数据从内核缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区,完成后通知线程。优点 :完全非阻塞,无轮询或等待。缺点 :实现复杂,依赖操作系统支持(如 Linux AIO 不完善)。应用场景 :文件操作或高吞吐场景(如 Java AsynchronousFileChannel)。
NIO
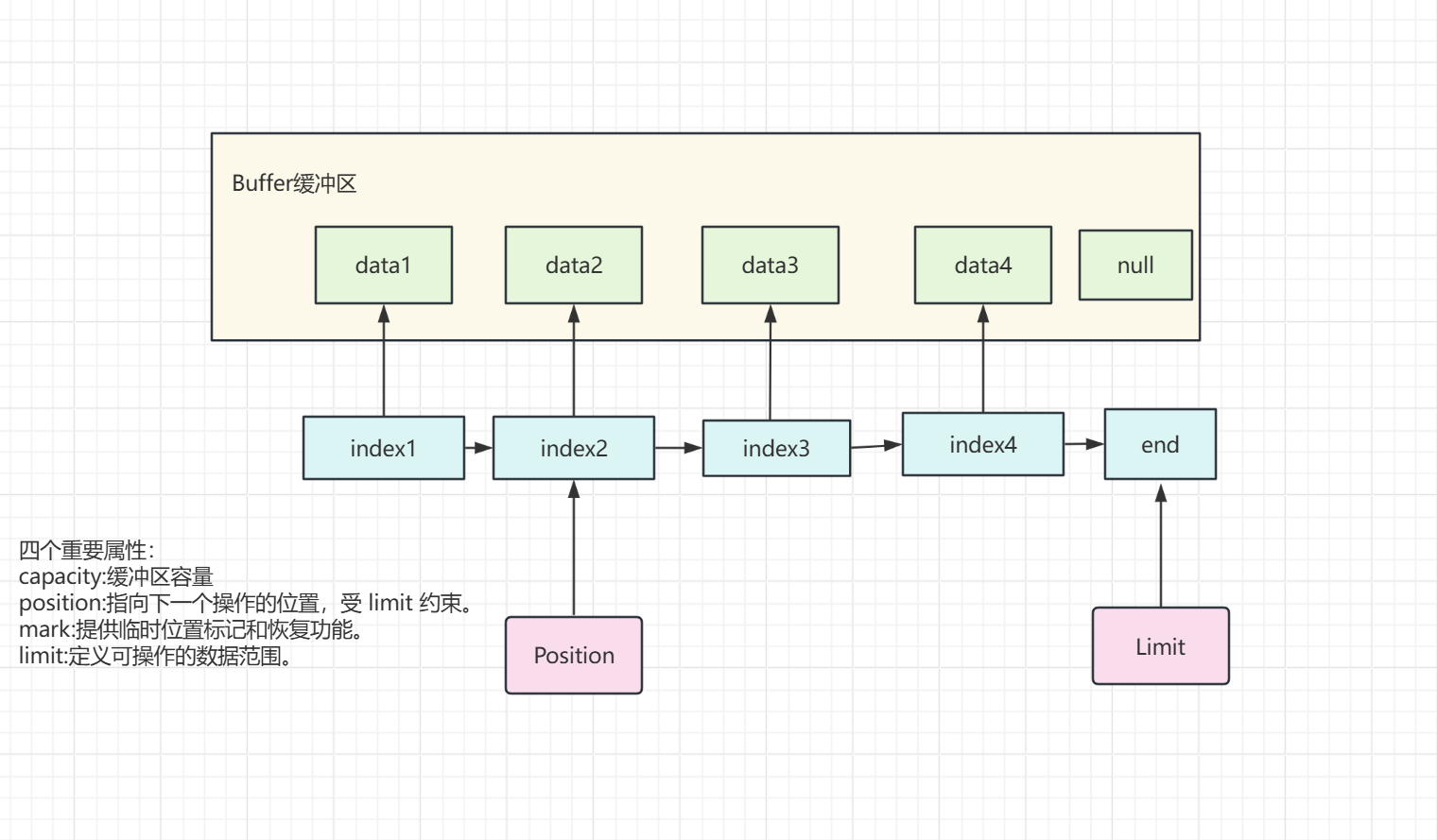
1.Buffer(缓冲区)
核心属性:
属性
描述
初始值
约束条件
capacity缓冲区的总容量(元素个数),创建时确定后不可修改。
由 allocate() 或 wrap() 确定
capacity ≥ 0
position下一个要读/写的索引位置。初始为 0,每读/写一个元素递增 1。
00 ≤ position ≤ limit
limit第一个不能读/写的索引(即读写操作的终点)。初始等于 capacity,可动态调整。
capacity0 ≤ limit ≤ capacity
mark标记一个临时位置,后续可通过 reset() 将 position 恢复到此值。默认未标记(-1)。
Buffer类是一个抽象类,有很多子类继承其方法完成特定数据的缓冲操作
Buffer类中包括的方法:
(1)核心方法: 这些方法用于管理缓冲区的核心属性:容量(Capacity) 、位置(Position) 、限制(Limit) 。
方法
说明
int capacity()返回缓冲区的总容量,创建后不可修改。
int position()返回当前读写位置(索引)。
Buffer position(int p)设置当前读写位置,需满足 0 ≤ p ≤ limit。
int limit()返回缓冲区的读写限制(position 不能超过此值)。
Buffer limit(int l)设置读写限制,需满足 0 ≤ l ≤ capacity。
(2)状态切换 用于在读模式 和写模式 之间切换缓冲区的状态。
方法
说明
Buffer clear()重置缓冲区为写模式:position=0, limit=capacity,数据未清除,但可被覆盖。
Buffer flip()切换为读模式:limit=position, position=0,通常在写入数据后调用。
Buffer rewind()重置 position=0,保持 limit 不变,用于重新读取数据。
Buffer compact()(子类实现,如 ByteBuffer)压缩缓冲区,将未读数据移到头部,准备继续写入。
(3)读写方法 用于向缓冲区写入数据(put)或从缓冲区读取数据(get),具体方法由子类实现。
1. 基本读写方法
方法
说明
ByteBuffer put(byte b)写入一个字节,position 递增。
ByteBuffer put(byte[] src)写入字节数组。
byte get()读取一个字节,position 递增。
ByteBuffer get(byte[] dst)读取字节到数组。
2.批量读写
方法
说明
Buffer put(Buffer src)将另一个缓冲区的数据复制到当前缓冲区。
Buffer get(byte[] dst, int offset, int length)从缓冲区读取数据到数组的指定位置。
(4)标记与重置 用于标记和恢复 position 的位置。
方法
说明
Buffer mark()标记当前 position,后续可通过 reset() 恢复到此位置。
Buffer reset()将 position 重置到之前标记的位置。
(5)工具方法
方法
说明
int remaining()返回剩余可操作的元素数量:limit - position。
boolean hasRemaining()检查是否还有剩余元素可操作(position < limit)。
boolean isReadOnly()判断缓冲区是否为只读。
boolean isDirect()(如 ByteBuffer)判断是否是直接内存(堆外内存)缓冲区。
(6)视图与复制 用于创建缓冲区的视图或副本,共享底层数据但独立维护属性。
方法
说明
Buffer duplicate()创建缓冲区的副本,共享数据但独立维护 position、limit 等属性。
Buffer slice()创建当前缓冲区的一个子视图,范围从 position 到 limit。
2.Channel 在 Java NIO 中,Channel(通道) 是用于在数据源(如文件、网络套接字)和缓冲区(Buffer)之间高效传输数据的抽象。它与传统 I/O 的流(InputStream/OutputStream)类似,但具有更强大的功能,如支持非阻塞模式、双向读写(部分实现)以及内存映射文件操作。
Channel在Java中是一个接口
1 2 3 4 5 public interface Channel extends Closeable { public boolean isOpen () ; public void close () throws IOException; }
区别(Channel和Stream): 1.Channel可以同时进行读写,流只能读或写
2.通道可以实现异步读写
3。通道可以写数据到缓冲区,也可以从缓冲区读数据
实现子类:
Channel 子类 应用场景 关键特性
FileChannel文件读写
内存映射、零拷贝传输
SocketChannelTCP 客户端通信
非阻塞模式、Selector 多路复用
ServerSocketChannelTCP 服务端监听
接受客户端连接
DatagramChannelUDP 数据报通信
无连接、支持广播
Pipe.Source/SinkChannel线程间通信
单向数据传输
AsynchronousFileChannel异步文件操作
回调或 Future 模式
AsynchronousSocketChannel异步 TCP 通信
非阻塞、高并发支持
FileChannel类 用于文件的读写、内存映射及零拷贝传输。
方法
说明
读写操作
int read(ByteBuffer dst)从通道读取数据到 ByteBuffer,返回实际读取的字节数(可能为 0)。
int write(ByteBuffer src)将 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入通道,返回实际写入的字节数。
定位与截断
long position()返回当前文件指针的位置。
FileChannel position(long newPosition)设置文件指针的位置(用于随机读写)。
FileChannel truncate(long size)截断文件到指定大小(丢弃超出部分)。
内存映射与零拷贝
MappedByteBuffer map(MapMode mode, long position, long size)将文件映射到内存,返回 MappedByteBuffer。模式包括:READ_ONLY、READ_WRITE、PRIVATE。
long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target)将文件数据从 position 开始的 count 字节直接传输到目标通道(零拷贝优化)。
long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count)从源通道读取数据,直接写入文件的指定位置(零拷贝优化)。
文件锁
FileLock lock()获取文件的独占锁(阻塞直到获取成功)。
FileLock tryLock()尝试非阻塞获取锁,失败返回 null。
SocketChannel类 (TCP 客户端)
方法
说明
boolean connect(SocketAddress remote)连接到服务端地址。在非阻塞模式下可能返回 false,需后续调用 finishConnect() 完成连接。
boolean finishConnect()完成非阻塞模式下的连接过程(需循环检查)。
boolean isConnected()检查是否已成功连接到服务端。
非阻塞模式
SocketChannel configureBlocking(boolean block)设置阻塞模式(true 为阻塞,默认值)。
注册到 Selector
SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops)将通道注册到 Selector,监听指定事件(如 SelectionKey.OP
ServerSocketChannel类 (TCP 服务端)
方法
说明
ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local)绑定到指定端口(如 new InetSocketAddress(8080))。
SocketChannel accept()接受客户端连接请求,返回对应的 SocketChannel(阻塞模式下会等待连接)。
非阻塞模式
configureBlocking(boolean block)设置非阻塞模式后,accept() 可能立即返回 null。
DatagramChannel类 (UDP 通信)
方法
说明
DatagramChannel bind(SocketAddress local)绑定本地端口接收数据(如 new InetSocketAddress(9090))。
int send(ByteBuffer src, SocketAddress target)发送数据包到目标地址。
SocketAddress receive(ByteBuffer dst)接收数据包到 ByteBuffer,返回发送方的地址。
3.Selector 用一个线程处理多个客户端连接,就会用到Selector,可以检测注册的多个通道中是否有事件发生,只有通道有读写事件发生时才会进行读写操作,不必为每个连接都创建线程,减少系统开销
Selector是一个抽象类
核心特点:
多路复用 :单线程可管理多个 Channel,减少线程资源消耗。非阻塞模式 :需将 Channel 设置为非阻塞模式(configureBlocking(false))才能注册到 Selector。事件驱动 :通过监听 SelectionKey 标识的事件(如 OP_READ、OP_WRITE)触发操作。
常用方法
方法
说明
static Selector open()创建一个新的 Selector 实例。
int select()阻塞等待至少一个已注册的 Channel 就绪事件,返回就绪事件的数量。
int select(long timeout)阻塞最多 timeout 毫秒,超时返回 0。
int selectNow()非阻塞检查就绪事件,立即返回当前就绪数量。
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys()返回已就绪的事件集合(需手动清理已处理的 SelectionKey)。
Set<SelectionKey> keys()返回所有注册到该 Selector 的 SelectionKey 集合(不可直接修改)。
Selector wakeup()唤醒因 select() 阻塞的线程。
void close()关闭 Selector 并释放资源。
聊天案例
服务端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 package com.itcast.nio.chat;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.*;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class Server { private static final Set<SocketChannel> clients = new HashSet <SocketChannel>(); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open(); server.bind(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); server.configureBlocking(false ); System.out.println("服务器启动成功" + server.getLocalAddress()); Selector selector = Selector.open(); server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); while (true ) { selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); if (key.isAcceptable()) { handleAccept(key, selector); }else if (key.isReadable()) { handleRead(key); } } } } public static void handleAccept (SelectionKey key, Selector selector) { try { ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel socketChannel = serverChannel.accept(); clients.add(socketChannel); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false ); socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); System.out.println("客户端连接: " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void handleRead (SelectionKey key) { SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); int bytesRead = 0 ; try { bytesRead = clientChannel.read(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); closeClient(clientChannel); return ; } if (bytesRead == -1 ) { closeClient(clientChannel); return ; } if (bytesRead > 0 ) { buffer.flip(); byte [] data = new byte [buffer.remaining()]; buffer.get(data); String message = new String (data).trim(); try { System.out.println("客户端收到消息 [" + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress() + "]: " + message); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } broadcastMessage(message, clientChannel); } } private static void broadcastMessage (String message, SocketChannel clientChannel) { if (clients.isEmpty()) return ; ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap((message + '\n' ).getBytes()); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap((message + "\n" ).getBytes()); for (SocketChannel client : clients) { if (client != clientChannel && client.isOpen()) { try { client.write(buffer); buffer.rewind(); } catch (IOException e) { closeClient(client); } } } } private static void closeClient (SocketChannel clientChannel) { clients.remove(clientChannel); try { System.out.println("客户端断开连接: " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress()); clientChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
客户端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 package com.itcast.nio.chat;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.net.SocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;import java.util.Scanner;public class Client { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { SocketChannel client = SocketChannel.open(); client.configureBlocking(false ); client.connect(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); System.out.println("连接服务器..." ); while (!client.finishConnect()) { Thread.sleep(100 ); System.out.println("等待连接..." ); } new Thread (() -> { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); while (true ) { try { int bytesRead = client.read(buffer); if (bytesRead > 0 ) { buffer.flip(); System.out.println("[群消息] " + new String (buffer.array(), 0 , bytesRead)); buffer.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { break ; } } }).start(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); while (true ) { String msg = scanner.nextLine(); client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes())); if ("exit" .equals(msg)) { break ; } } } }
零拷贝 什么是零拷贝?
零拷贝(Zero-copy)技术指在计算机执行操作时,CPU 不需要先将数据从⼀个内存区域复制到另⼀个内存区域 ,从⽽可以减少上下⽂切换以及 CPU 的拷贝时间。它的作用是在数据从网络设备到⽤户程序空间传递的过程中,减少数据拷贝次数,减少系统调用,实现 CPU 的零参与,彻底消除 CPU 在这方面的负载 。
实现零拷贝用到的最主要技术是 DMA 数据传输技术 和内存区域映射技术 。
零拷贝机制可以减少数据在内核缓冲区和⽤户进程缓冲区之间反复的 I/O 拷贝操作。零拷贝机制可以减少用户进程地址空间和内核地址空间之间因为上下⽂切换⽽带来的 CPU 开销。在 Java 程序中,常⽤的零拷贝有 mmap(内存映射)和 sendFile。
源自:https://www.cnblogs.com/liconglong/p/15211413.html
传统 I/O 的数据拷贝流程 4 次上下文切换 + 4 次数据拷贝(其中 2 次由 CPU 参与),效率较低。
在传统 I/O 操作中(例如从文件读取数据并发送到网络),数据需要经历多次拷贝和上下文切换:
磁盘 → 内核缓冲区 :数据从磁盘读取到内核空间的缓冲区(通过 DMA 技术)。内核缓冲区 → 用户缓冲区 :数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间的应用程序缓冲区(需要 CPU 参与)。用户缓冲区 → Socket 缓冲区 :应用程序将数据从用户缓冲区拷贝到内核空间的 Socket 缓冲区(再次 CPU 参与)。Socket 缓冲区 → 网卡 :数据从 Socket 缓冲区发送到网络设备(通过 DMA)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class FileDemoServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File ("file/test01.txt" ); RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile (file, "rw" ); byte [] bytes = new byte [(int ) file.length()]; randomAccessFile.read(bytes); ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket (3333 ); Socket client = server.accept(); OutputStream outputStream = client.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write(bytes); outputStream.close(); } } public class FileDemoClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket (); socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 ]; inputStream.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String (bytes)); } }
零拷贝的两种常见实现
sendfile 系统调用
数据直接从文件描述符传输到 Socket 描述符,无需用户态参与。
适用于文件到网络的传输(如 HTTP 文件下载)。
内存映射文件(mmap) :
将文件映射到用户态虚拟内存,用户程序直接操作内存,减少拷贝次数。
适用于需要频繁修改文件的场景(如数据库)
mmap 和 sendFile 的区别 1.mmap 适合小数据量读写,sendFile 适合大文件传输。
2.mmap 需要 4 次上下文切换,3 次数据拷贝;sendFile 需要 3 次上下文切换,最少 2 次数据拷贝。
3.sendFile 可以利用 DMA 方式,减少 CPU 拷贝,mmap 则不能(必须从内核拷贝到 Socket 缓冲区)。
传统 I/O vs NIO 零拷贝的对比
步骤 传统 I/O NIO + 零拷贝
数据拷贝次数 4 次(2 次用户态↔内核态)
2 次(仅内核态内拷贝)
CPU 参与次数 2 次(用户态↔内核态拷贝)
0 次(DMA 完成)
上下文切换次数 4 次(读/写各 2 次)
2 次(系统调用发起和完成)
典型实现 FileInputStream.read() + Socket.send()FileChannel.transferTo()
DMA和内存映射
技术 核心作用 应用场景
DMA 外设与内存直接传输数据,减少 CPU 参与
磁盘 I/O、网络通信、GPU 渲染
内存区域映射 将外设或文件映射到内存,实现零拷贝访问
文件高效读写、硬件控制、进程间通信
零拷贝性能分析 (服务端向客户端发送大文件)
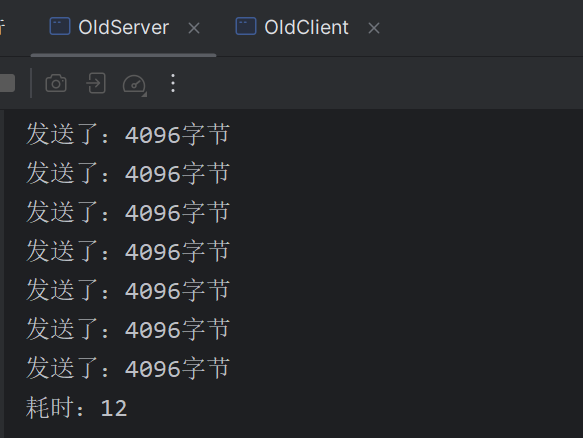
不使用零拷贝: OldServer.class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class OldServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open(); server.bind(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); server.configureBlocking(false ); Selector selector = Selector.open(); server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (SelectionKey selectionKey : selectionKeys) { if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) { handle(selectionKey, selector); } } long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗时:" + (t2 - t1)); } public static void handle (SelectionKey key, Selector selector) throws IOException { File file = new File ("file/protoc-3.6.1-win32.zip" ); ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel client = server.accept(); client.configureBlocking(false ); client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream (file); while (true ) { if (fileInputStream.available() == 0 ) { break ; } byte [] bytes = new byte [4096 ]; fileInputStream.read(bytes); int sum = client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes)); System.out.println("发送了:" + sum + "字节" ); } fileInputStream.close(); client.close(); } }
OldClient.class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class OldClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { SocketChannel client = SocketChannel.open(); client.configureBlocking(false ); client.connect(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); System.out.println("连接服务器..." ); while (!client.finishConnect()) { Thread.sleep(100 ); System.out.println("等待连接完成..." ); } System.out.println("连接完成..." ); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (true ) { byte [] bytes = new byte [4096 ]; ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); int read = client.read(buffer); if (read == -1 ) break ; } long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗时:" + (t2 - t1)); } }
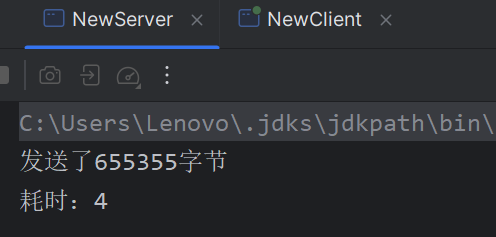
使用零拷贝: NewServer.class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class NewServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open(); server.configureBlocking(false ); server.bind(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); Selector selector = Selector.open(); server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (SelectionKey selectionKey : selectionKeys) { if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) { handle(selectionKey, selector); } } long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗时:" + (t2 - t1)); } public static void handle (SelectionKey key, Selector selector) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel client = server.accept(); client.configureBlocking(false ); client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); String filename = "file/protoc-3.6.1-win32.zip" ; FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream (filename).getChannel(); long sum = channel.transferTo(0 , channel.size(), client); System.out.println("发送了" + sum + "字节" ); } }
NewClient.class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class NewClient { public static void main (String[] args) { SocketChannel client = null ; try { client = SocketChannel.open(); client.configureBlocking(false ); client.connect(new InetSocketAddress (3333 )); System.out.println("连接服务器..." ); if (!client.finishConnect()) { Thread.sleep(100 ); System.out.println("正在连接中。。。" ); } ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096 ); while (true ) { int read = 0 ; try { read = client.read(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { client.close(); } if (read == -1 ) { System.out.println("服务端已关闭连接" ); break ; } if (read > 0 ) { System.out.println("收到服务端的消息:" + new String (buffer.array(), 0 , read)); buffer.clear(); } else { Thread.sleep(100 ); } } client.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("连接已关闭" ); } }
性能比较:
很显然零拷贝性能要高很多
Reactor模式 什么是Reactor模式? Reactor 模式是一种事件驱动模型,核心思想是 通过一个或多个线程监听 I/O 事件(如连接、读写),并将事件分发给对应的处理器 。常见的 Reactor 变体包括:
单 Reactor 单线程 :所有操作(连接、I/O)由一个线程完成,简单但性能受限。单 Reactor 多线程 :主线程处理连接,I/O 操作交给线程池,但主线程可能成为瓶颈。主从 Reactor 多线程 :主 Reactor 处理连接,子 Reactor 处理 I/O,Netty 默认采用此模式。
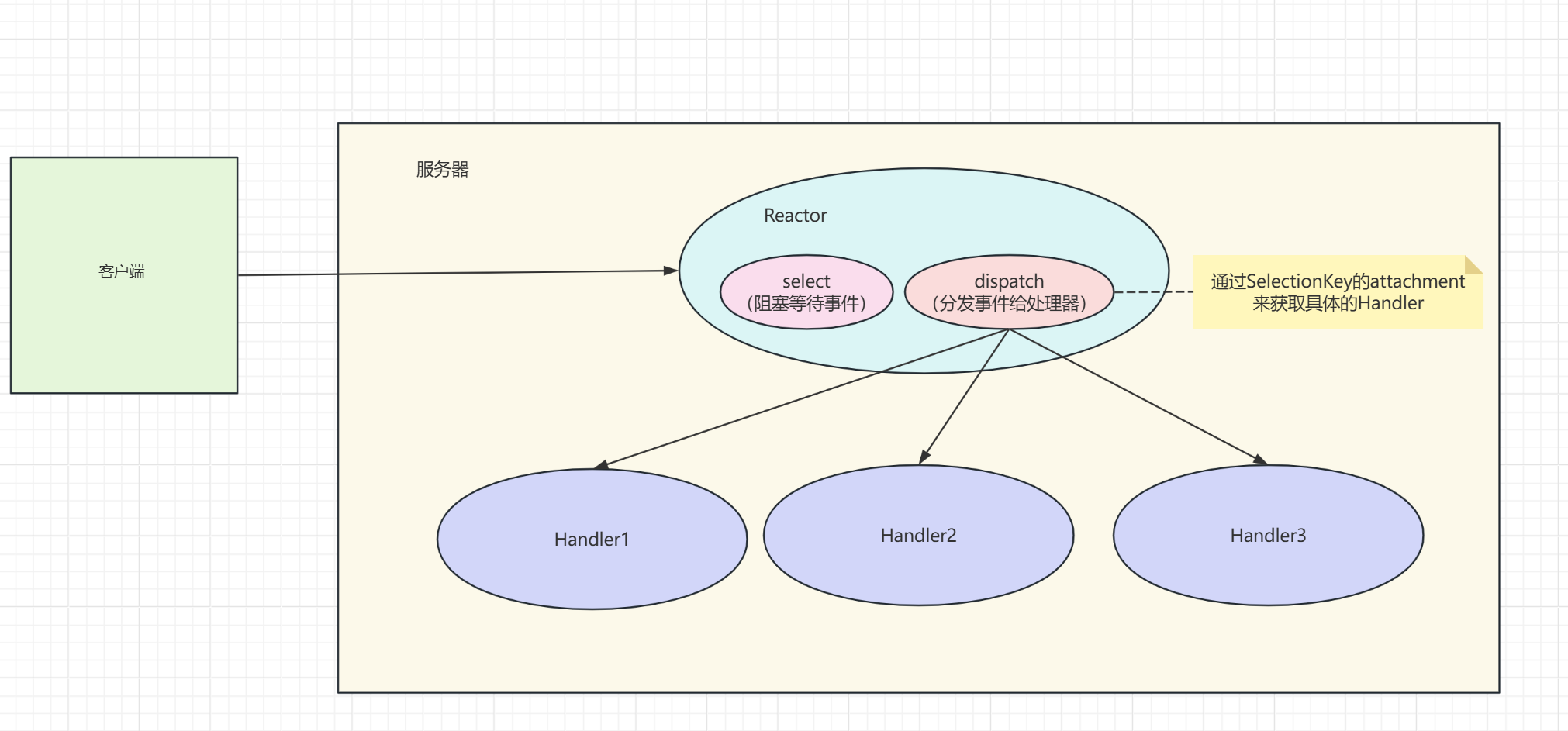
理解: reactor可以认为是一种设计模式,用于处理客户端的事件,主要是通过select和dispatch操作来监听事件发生和处理事件
主要逻辑:
1.服务器注册到selector中,为其连接事件分配一个Handler(其实是一个Runnable对象, 名称可以定义为Acceptor)
2.Reactor监听事件发生,当事件发生时,会通过dispatch将时间分发给具体的处理器
3.dispatch通过SelectionKey(可以认为是selector实例对象中的事件id)的attachment来获取具体的Handler
4.执行具体的Handler逻辑
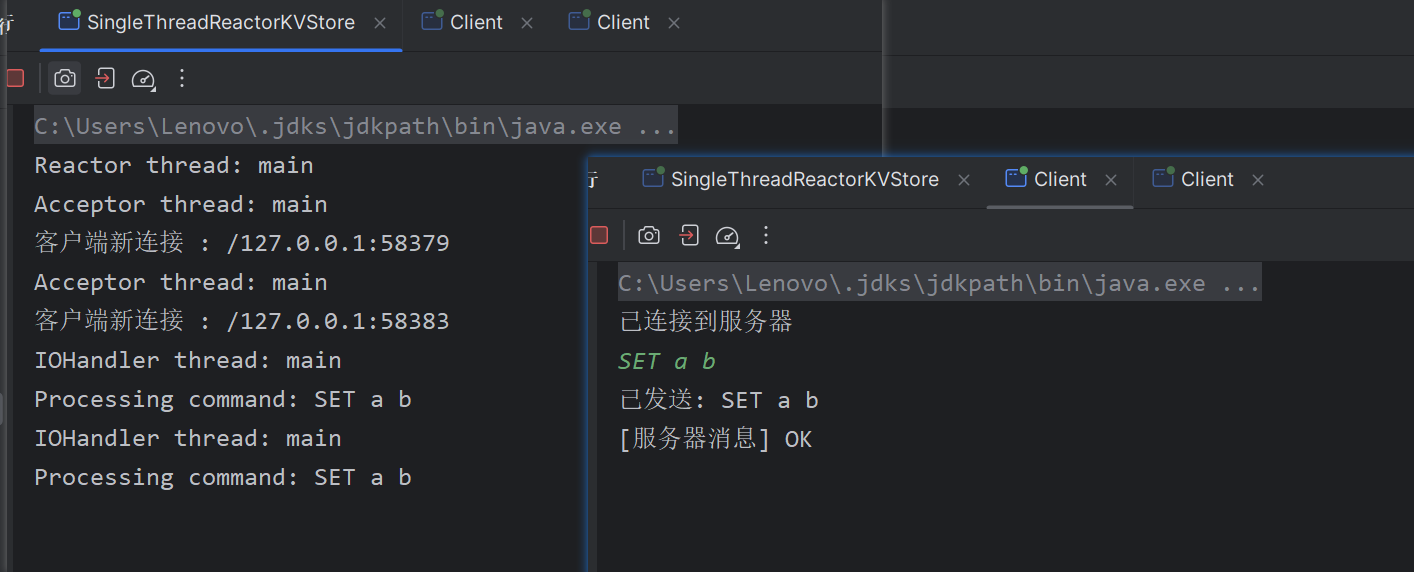
单Reactor单线程 键值存储服务器: SingleThreadReactorKVStore.class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;import java.nio.channels.Selector;import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;public class SingleThreadReactorKVStore { private final Selector selector; private final ServerSocketChannel serverChannel; private final Map<String, String> store = new HashMap <>(); public SingleThreadReactorKVStore (int port) throws IOException { selector = Selector.open(); serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress (port)); serverChannel.configureBlocking(false ); serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, new Acceptor ()); } public void start () { System.out.println("Reactor thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { while (!Thread.interrupted()) { selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = it.next(); dispatch(key); it.remove(); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { serverChannel.close(); selector.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void dispatch (SelectionKey key) { Runnable handler = (Runnable) key.attachment(); if (handler != null ) { handler.run(); } } private class Acceptor implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { System.out.println("Acceptor thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept(); System.out.println("客户端新连接 : " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress()); if (clientChannel != null ) { new IOHandler (clientChannel); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private class IOHandler implements Runnable { private final SocketChannel channel; private final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); public IOHandler (SocketChannel channel) throws IOException { this .channel = channel; channel.configureBlocking(false ); channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, this ); } @Override public void run () { System.out.println("IOHandler thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { if (!channel.isOpen()) return ; buffer.clear(); int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer); if (bytesRead == -1 ) { channel.close(); return ; } buffer.flip(); String request = new String (buffer.array(), 0 , buffer.limit()).trim(); String response = processCommand(request); ByteBuffer respBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap((response + "\n" ).getBytes()); channel.write(respBuffer); } catch (IOException e) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } } private String processCommand (String request) { System.out.println("Processing command: " + request); String[] parts = request.split(" " ); if (parts.length < 2 ) return "ERROR: Invalid command" ; String cmd = parts[0 ].toUpperCase(); String key = parts[1 ]; switch (cmd) { case "SET" : if (parts.length < 3 ) return "ERROR: Missing value" ; store.put(key, parts[2 ]); return "OK" ; case "GET" : return store.getOrDefault(key, "(nil)" ); default : return "ERROR: Unknown command" ; } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { SingleThreadReactorKVStore server = new SingleThreadReactorKVStore (3333 ); server.start(); } }
Client.class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;public class Client { private static final AtomicBoolean isConnected = new AtomicBoolean (true ); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false ); socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress ("localhost" , 3333 )); while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) { System.out.println("等待连接完成..." ); } System.out.println("已连接到服务器" ); Thread readThread = new Thread (() -> { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); try { while (isConnected.get()) { int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer); if (bytesRead == -1 ) { System.out.println("[服务器已关闭连接]" ); isConnected.set(false ); break ; } else if (bytesRead > 0 ) { buffer.flip(); System.out.println("[服务器消息] " + new String (buffer.array(), 0 , bytesRead)); buffer.clear(); } } } catch (IOException e) { if (isConnected.get()) { System.err.println("连接异常: " + e.getMessage()); isConnected.set(false ); } } finally { closeChannel(socketChannel); } }); readThread.start(); try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in)) { while (isConnected.get()) { String line = scanner.nextLine(); if ("exit" .equals(line)) break ; if (!isConnected.get()) { System.out.println("连接已断开,无法发送消息" ); break ; } ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(line.getBytes()); try { socketChannel.write(buffer); System.out.println("已发送: " + line); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("发送失败: " + e.getMessage()); isConnected.set(false ); break ; } } } closeChannel(socketChannel); } private static void closeChannel (SocketChannel channel) { try { if (channel != null && channel.isOpen()) { channel.close(); System.out.println("连接已关闭" ); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:
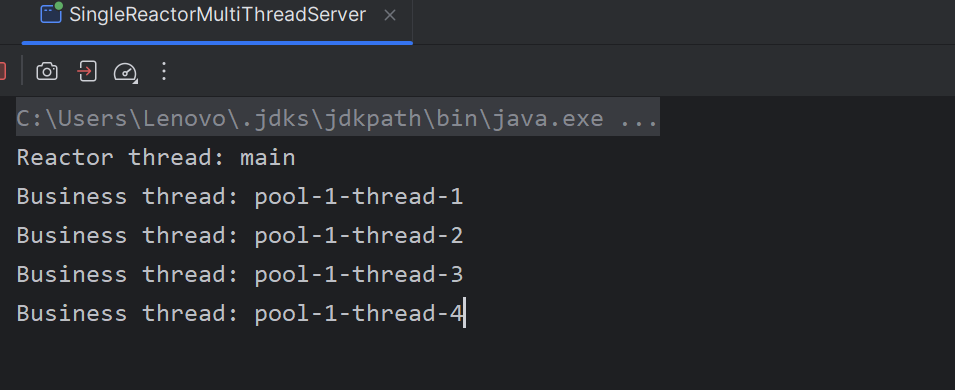
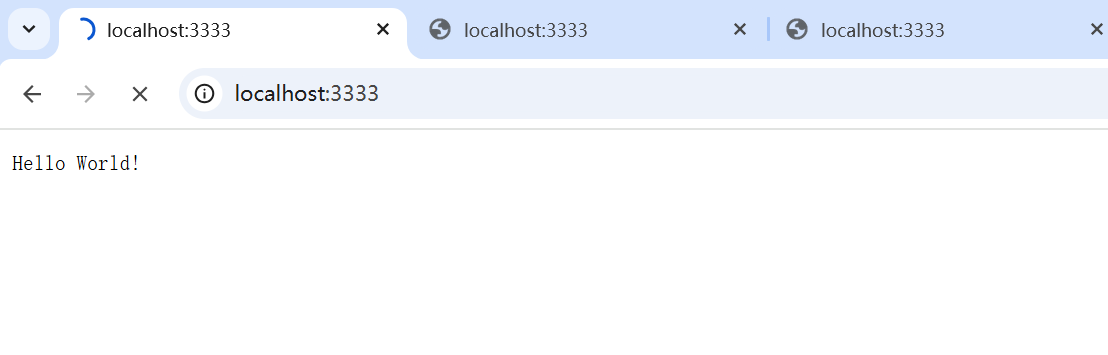
单 Reactor 多线程 简单HTTP 服务器: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.*;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class SingleReactorMultiThreadServer { private final Selector selector; private final ServerSocketChannel serverChannel; private final ExecutorService businessPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4 ); public SingleReactorMultiThreadServer (int port) throws IOException { selector = Selector.open(); serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress (port)); serverChannel.configureBlocking(false ); serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, new Acceptor ()); } public void start () { System.out.println("Reactor thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { while (!Thread.interrupted()) { selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = it.next(); dispatch(key); it.remove(); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void dispatch (SelectionKey key) { Runnable handler = (Runnable) key.attachment(); if (handler != null ) { handler.run(); } } private class Acceptor implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { try { SocketChannel client = serverChannel.accept(); new IOHandler (client); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private class IOHandler implements Runnable { private final SocketChannel channel; private final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); public IOHandler (SocketChannel channel) throws IOException { this .channel = channel; channel.configureBlocking(false ); channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, this ); } @Override public void run () { try { if (!channel.isOpen()) return ; buffer.clear(); int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer); if (bytesRead == -1 ) { channel.close(); return ; } buffer.flip(); String request = new String (buffer.array(), 0 , buffer.limit()); if (request.startsWith("GET" )) { businessPool.submit(() -> { try { processRequest(request); } catch (ClosedChannelException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } } catch (IOException e) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } } private void processRequest (String request) throws ClosedChannelException { System.out.println("Business thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(100 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } String response = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Length: 12\r\n\r\nHello World!" ; channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, new WriteHandler (channel, response)); } } private class WriteHandler implements Runnable { private final SocketChannel channel; private final String response; public WriteHandler (SocketChannel channel, String response) { this .channel = channel; this .response = response; } @Override public void run () { try { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes()); channel.write(buffer); channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { SingleReactorMultiThreadServer server = new SingleReactorMultiThreadServer (3333 ); server.start(); }
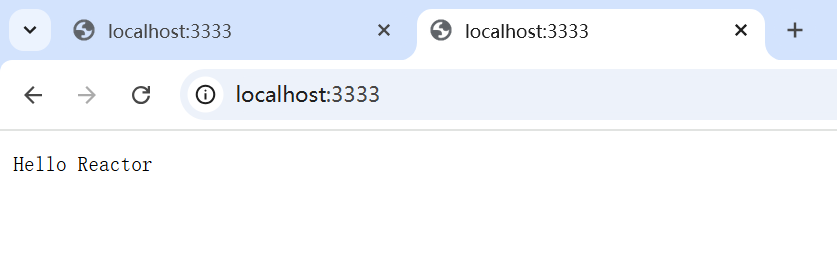
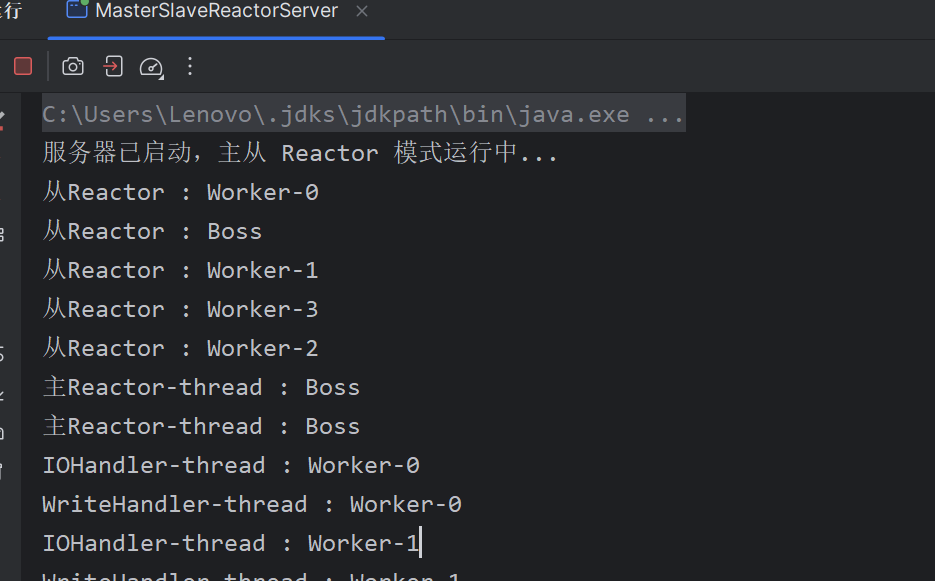
主从 Reactor 多线程案例 简易Http服务器: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.*;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Queue;import java.util.Set;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class MasterSlaveReactorServer { private final Reactor bossReactor; private final Reactor[] workerReactors; private final AtomicInteger workerIndex = new AtomicInteger (0 ); private final ExecutorService businessPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4 ); public MasterSlaveReactorServer (int port, int workerCount) throws IOException { bossReactor = new Reactor ("Boss" ); workerReactors = new Reactor [workerCount]; for (int i = 0 ; i < workerCount; i++) { workerReactors[i] = new Reactor ("Worker-" + i); } ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress (port)); serverChannel.configureBlocking(false ); bossReactor.register(serverChannel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, new Acceptor (serverChannel)); } public void start () { bossReactor.start(); for (Reactor worker : workerReactors) { worker.start(); } } private class Acceptor implements Runnable { private final ServerSocketChannel serverChannel; public Acceptor (ServerSocketChannel serverChannel) { this .serverChannel = serverChannel; } @Override public void run () { System.out.println("主Reactor-thread : " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept(); if (clientChannel != null ) { int index = workerIndex.getAndIncrement() % workerReactors.length; Reactor worker = workerReactors[index]; worker.registerChannel(clientChannel); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private class Reactor extends Thread { private final Selector selector; private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue <>(); public Reactor (String name) throws IOException { super (name); selector = Selector.open(); } public void registerChannel (SocketChannel channel) { addTask(() -> { try { channel.configureBlocking(false ); SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); key.attach(new IOHandler (channel, key)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); selector.wakeup(); } public void addTask (Runnable task) { taskQueue.offer(task); } @Override public void run () { System.out.println("从Reactor : " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { while (!Thread.interrupted()) { selector.select(1000 ); processSelectedKeys(); processPendingTasks(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void processSelectedKeys () throws IOException { Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = it.next(); it.remove(); if (key.isValid()) { Runnable handler = (Runnable) key.attachment(); if (handler != null ) { handler.run(); } } } } private void processPendingTasks () { Runnable task; while ((task = taskQueue.poll()) != null ) { task.run(); } } public void register (ServerSocketChannel serverChannel, int opAccept, Acceptor acceptor) { try { serverChannel.configureBlocking(false ); serverChannel.register(selector, opAccept, acceptor); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private class IOHandler implements Runnable { private final SocketChannel channel; private final SelectionKey key; private final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 ); public IOHandler (SocketChannel channel, SelectionKey key) { this .channel = channel; this .key = key; } @Override public void run () { System.out.println("IOHandler-thread : " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { if (!channel.isOpen()) return ; if (key.isReadable()) { buffer.clear(); int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer); if (bytesRead == -1 ) { channel.close(); return ; } buffer.flip(); String request = new String (buffer.array(), 0 , buffer.limit()); businessPool.submit(() -> processRequest(request)); } } catch (IOException e) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } } private void processRequest (String request) { try { Thread.sleep(100 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } String response = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Length: 13\r\n\r\nHello Reactor!" ; key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); key.attach(new WriteHandler (channel, response)); key.selector().wakeup(); } } private class WriteHandler implements Runnable { private final String response; private final SocketChannel channel; public WriteHandler (SocketChannel channel, String response) { this .channel = channel; this .response = response; } @Override public void run () { System.out.println("WriteHandler-thread : " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(response.getBytes()); channel.write(buffer); channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { MasterSlaveReactorServer server = new MasterSlaveReactorServer (3333 , 4 ); server.start(); System.out.println("服务器已启动,主从 Reactor 模式运行中..." ); } }
Netty 介绍
Netty 是一个 NIO 客户端服务器框架 ,可以快速轻松地开发网络应用程序(例如协议服务器和客户端)。它极大地简化了 TCP 和 UDP 套接字服务器等网络编程。
它基于 Java NIO(Non-blocking I/O)技术,简化了网络编程的复杂性,广泛应用于实时通信、游戏服务器、分布式系统等领域(如 Dubbo、RocketMQ 等框架的底层通信)。
官方文档:https://netty.io/4.2/api/index.html
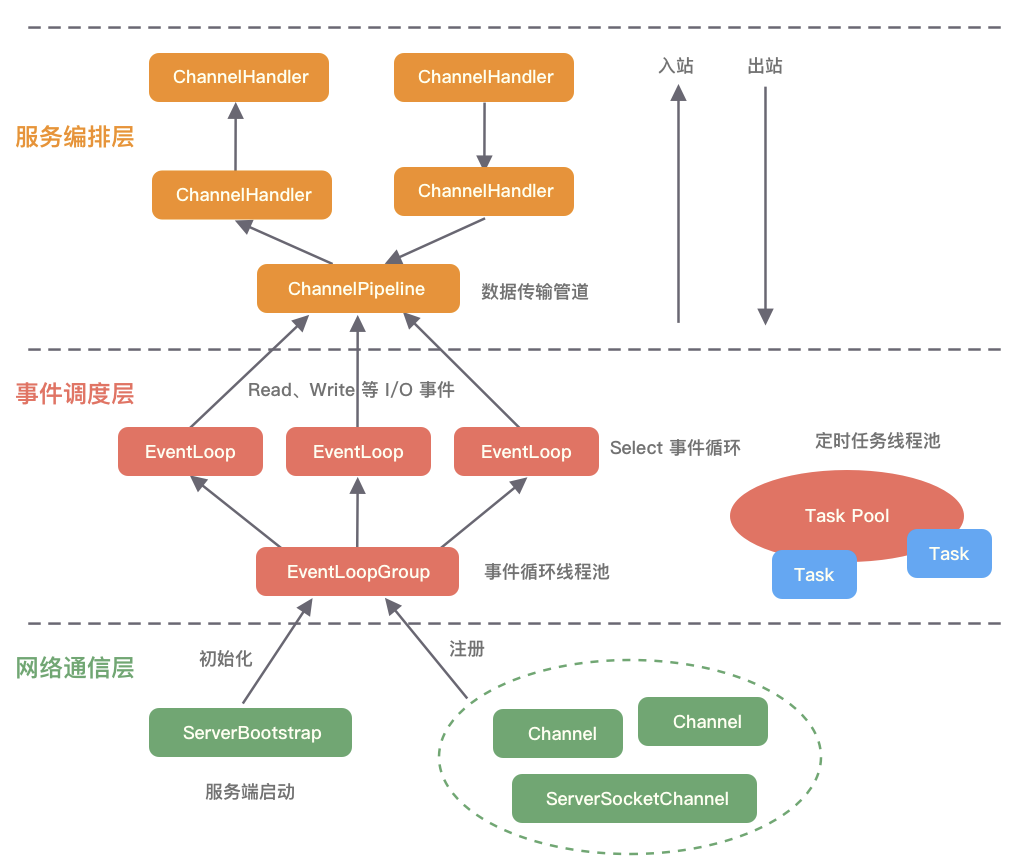
图源:https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1708060/202111/1708060-20211110224700852-1182764791.png
Netty启动流程:
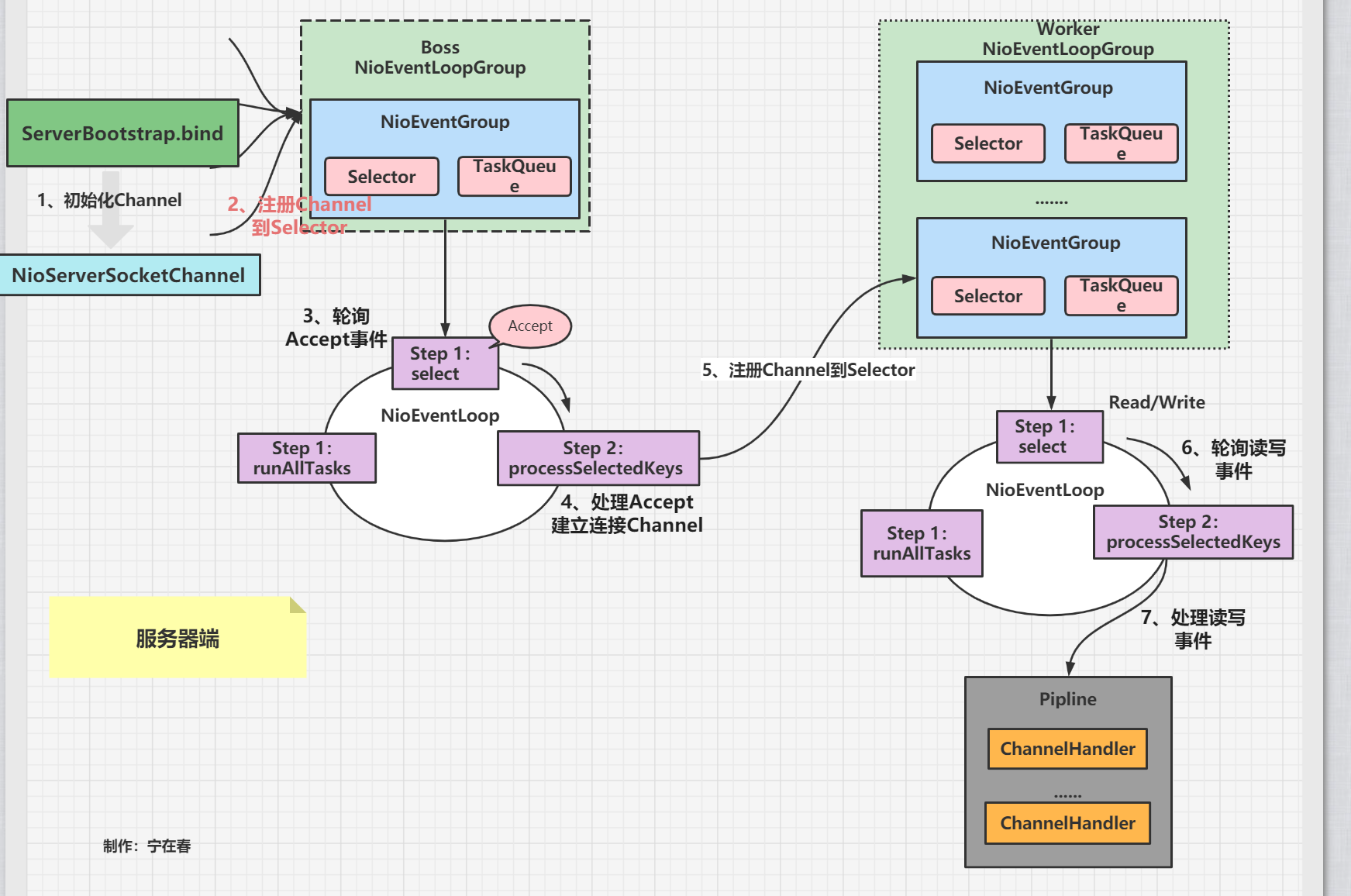
图源:https://cloud.tencent.cn/developer/article/2146079
线程模式 Netty 基于 Reactor 模式设计,主要有三种线程模型:
单线程模型 :所有 IO 操作由一个线程处理多线程模型 :Acceptor 和 IO 处理器分离为不同线程组主从多线程模型 :Acceptor 也使用线程池处理
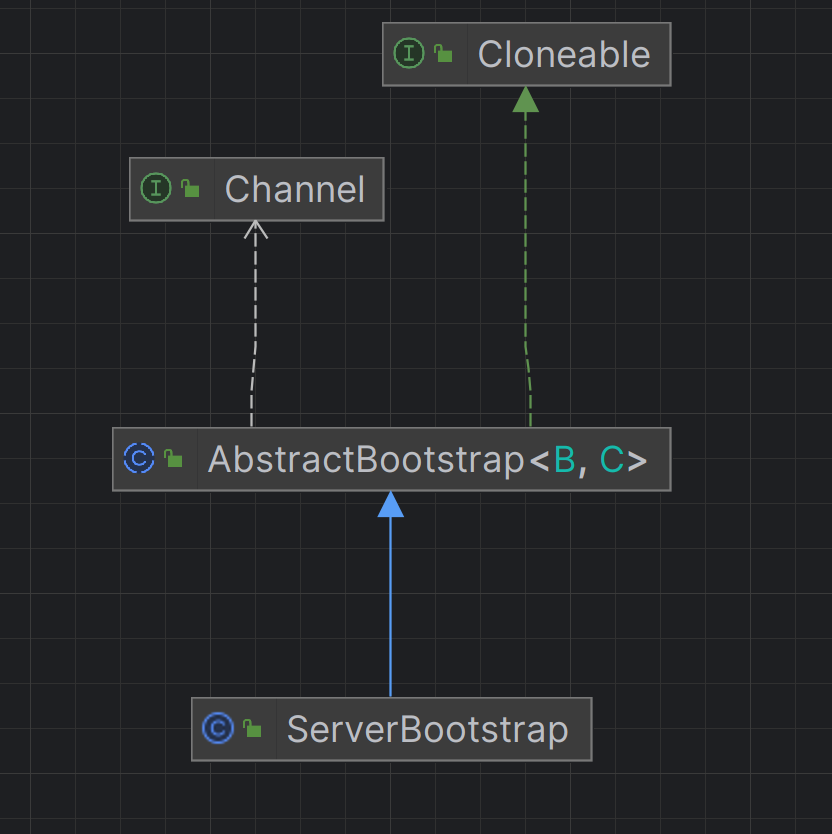
核心组件 ServerBootstrap(服务器启动类) 核心作用
用于配置和启动 Netty 服务器。
管理两个EventLoopGroup:BossGroup(接受连接)和 WorkerGroup(处理 IO)。
关键方法
group(EventLoopGroup bossGroup, EventLoopGroup workerGroup):设置主从线程组。channel(Class<? extends ServerChannel> channelClass):设置服务器通道类型(如NioServerSocketChannel)。childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler):设置子通道处理器(客户端连接的 Pipeline)。option(ChannelOption option, T value):设置服务器通道选项(如SO_BACKLOG)。childOption(ChannelOption option, T value):设置子通道选项(如SO_KEEPALIVE)。bind(int port):绑定端口并启动服务器。
Bootstrap(客户端启动类) 核心作用
用于配置和启动 Netty 客户端。
只需要一个EventLoopGroup处理所有连接和 IO 操作。
关键方法
group(EventLoopGroup group):设置线程组。channel(Class<? extends Channel> channelClass):设置客户端通道类型(如NioSocketChannel)。handler(ChannelHandler handler):设置通道处理器(客户端 Pipeline)。option(ChannelOption option, T value):设置通道选项(如SO_KEEPALIVE)。connect(String host, int port):连接到远程服务器。
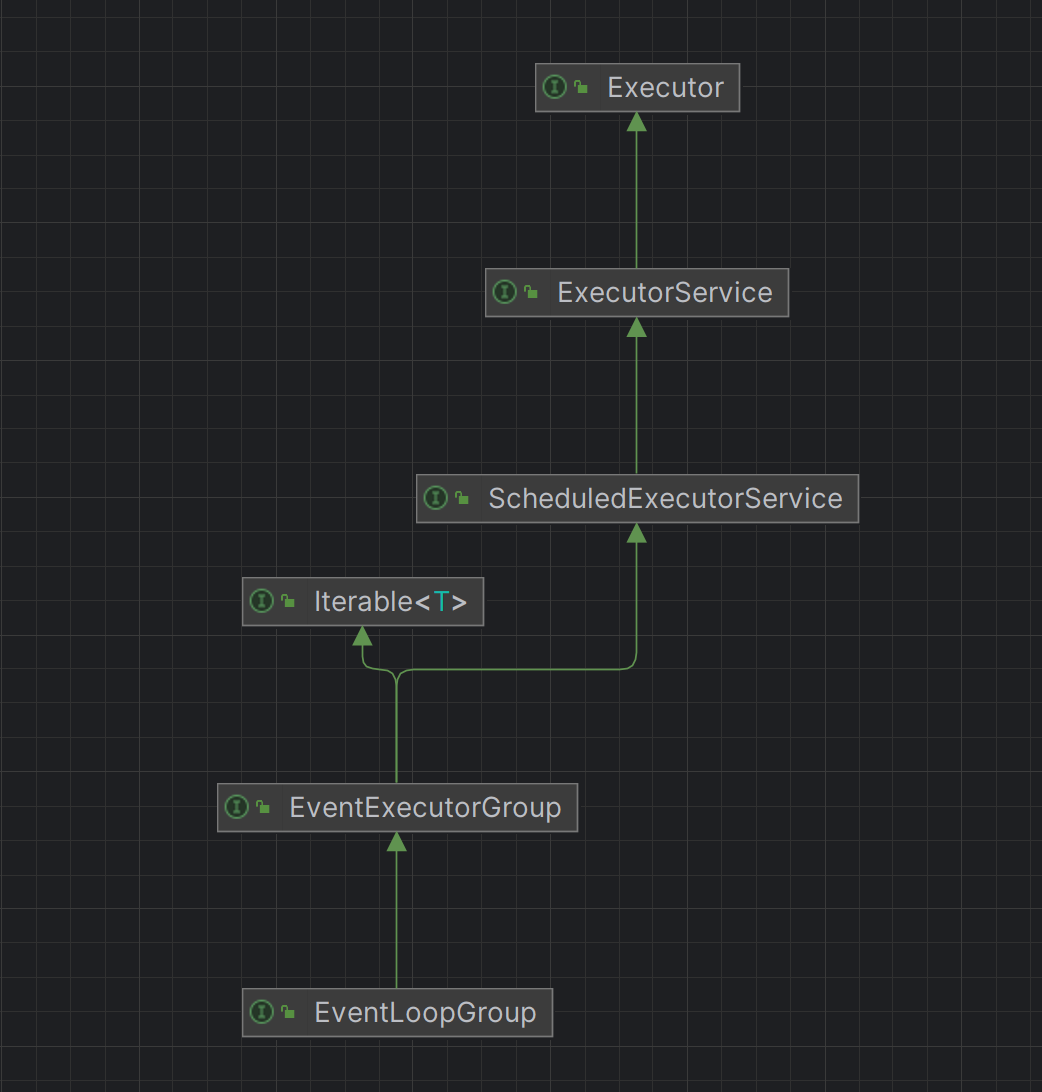
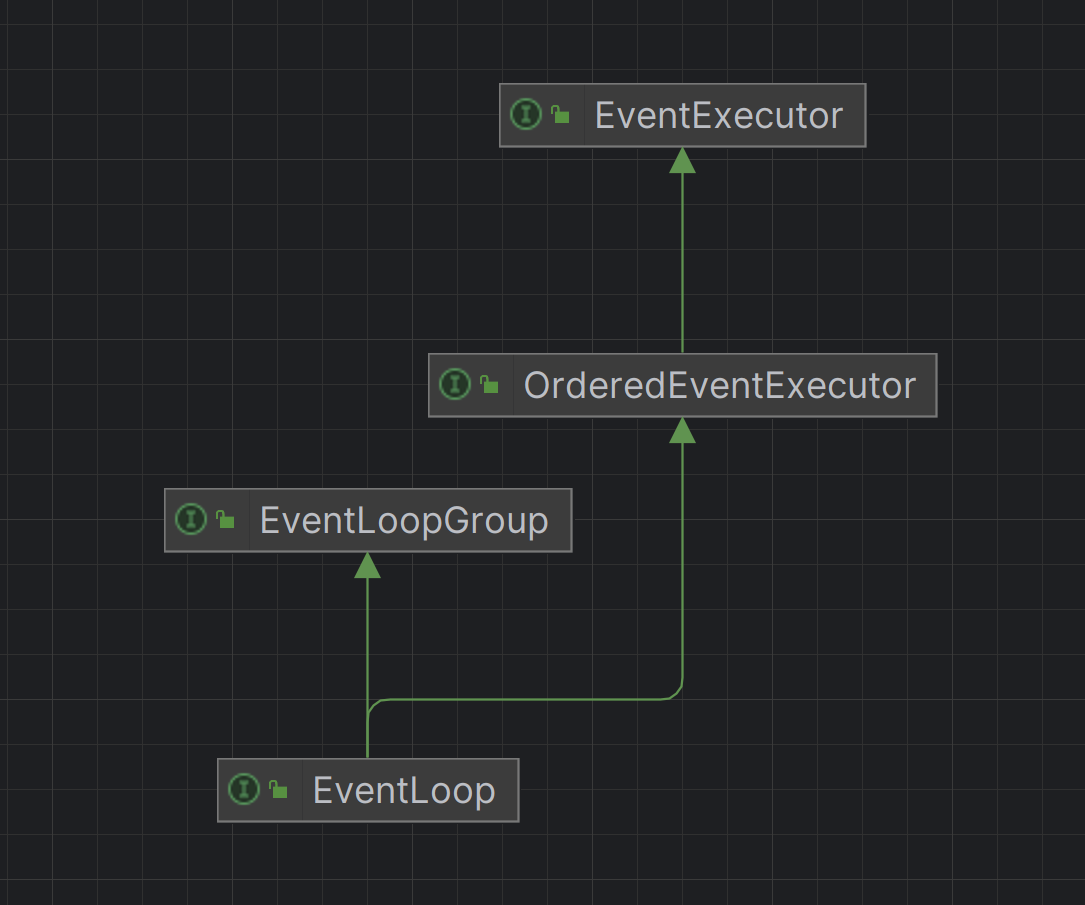
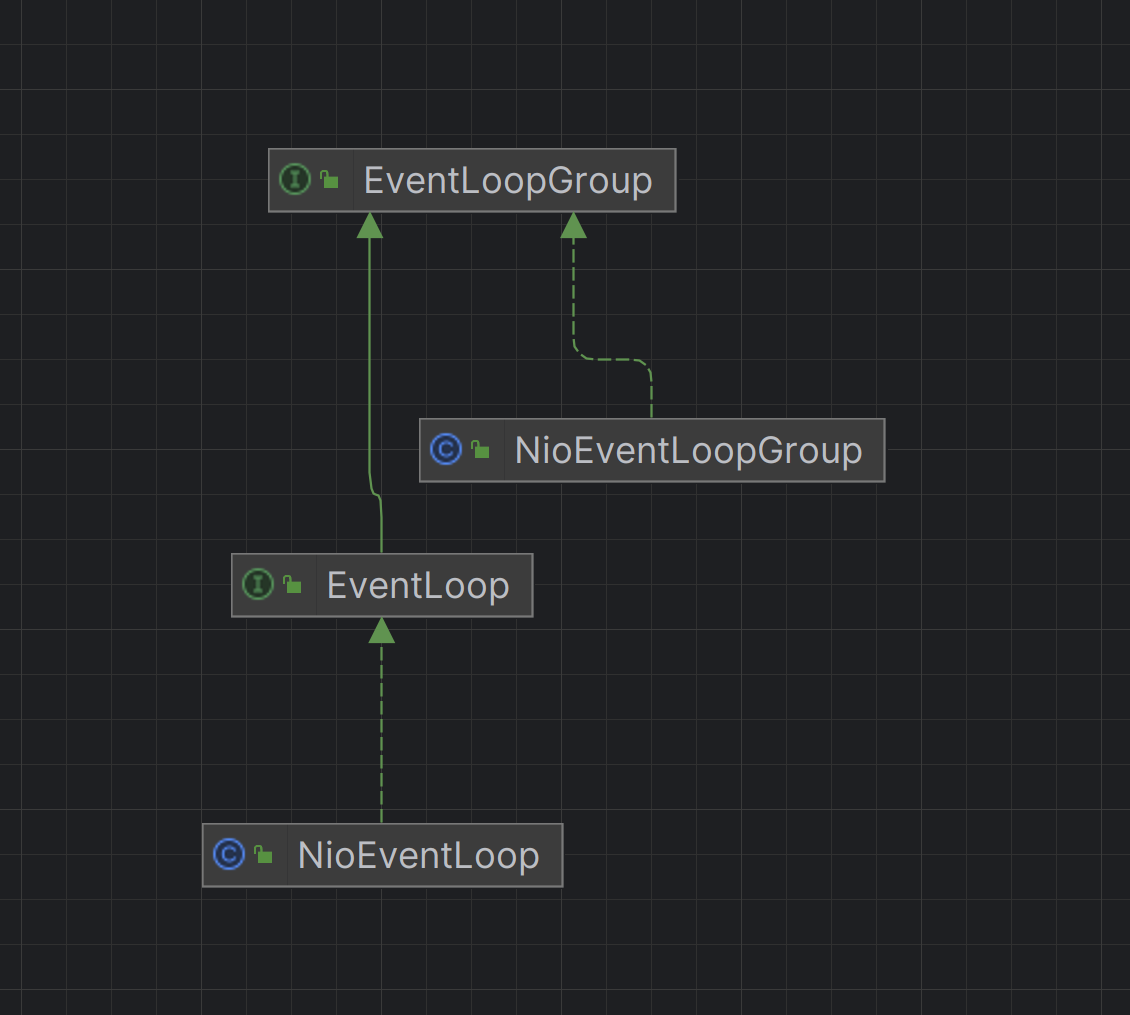
EventLoopGroup 与 EventLoop
EventLoopGroup :线程池,管理多个EventLoop。EventLoop :单线程执行器,负责处理 IO 事件(连接、读写)和任务队列。
分类
NioEventLoopGroup :基于 Java NIO,跨平台。EpollEventLoopGroup :基于 Linux epoll,性能更高。
Channel
NioSocketChannel:客户端 TCP 连接。NioServerSocketChannel:服务器 TCP 监听。NioDatagramChannel:UDP 连接。
ChannelPipeline
入站(Inbound) :数据从网络到应用(如channelRead())。出站(Outbound) :数据从应用到网络(如write())。
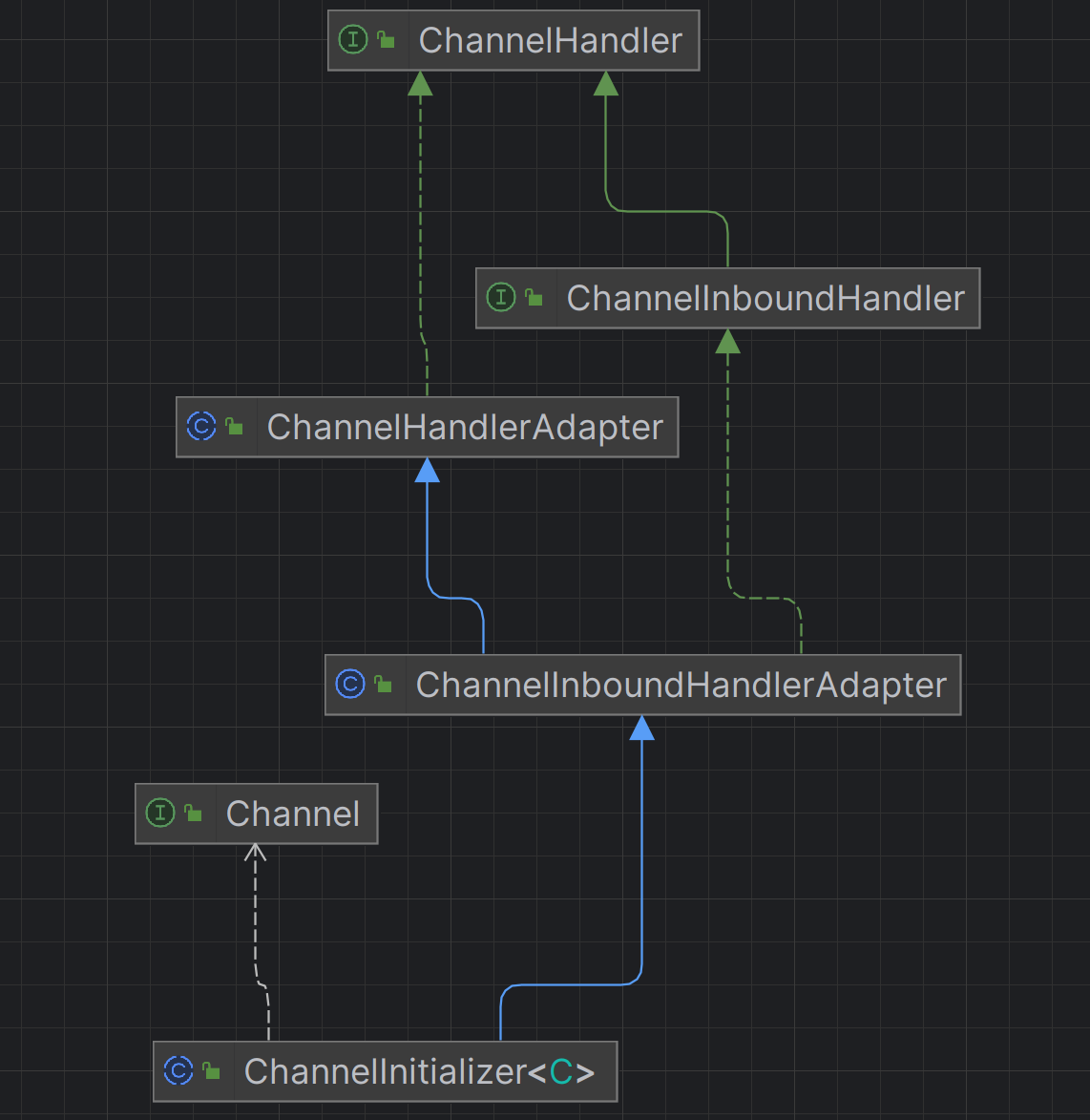
ChannelHandler
ChannelInboundHandler :处理入站数据。ChannelOutboundHandler :处理出站数据。
关键接口/抽象类:
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter :入站处理器基类。ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter :出站处理器基类。SimpleChannelInboundHandler :自动释放资源的入站处理器。
案例分析(群聊系统): 服务器: ChatServer.class 服务器启动类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 package com.itcast.netty.chat;import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;public class ChatServer { private final int port; public ChatServer (int port) { this .port = port; } public void run () throws InterruptedException { NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup (); NioEventLoopGroup workGroups = new NioEventLoopGroup (5 ); try { ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap (); server.group(bossGroup, workGroups); server.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); server.handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioServerSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioServerSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.INFO)); } }); server.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new StringDecoder (), new StringEncoder (), new ChatServerHandler (), new ChatConnectionServerHandler () ); } }); server.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ); ChannelFuture serverChannel = server.bind(port).sync(); serverChannel.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { workGroups.shutdownGracefully(); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } public static void main (String[] args) { ChatServer chatServer = new ChatServer (3333 ); try { chatServer.run(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
ChatServerHandler.class 处理客户端发来的信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package com.itcast.netty.chat;import io.netty.channel.Channel;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;import java.net.SocketAddress;import java.util.HashSet;public class ChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <String> { @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String msg) { SocketAddress socketAddress = channelHandlerContext.channel().remoteAddress(); for (Channel channel : ChatConnectionServerHandler.onlineUsers) { if (!channel.remoteAddress().equals(socketAddress)) { channel.writeAndFlush(socketAddress + "说: " + msg); } } } }
ChatConnectionServerHandler.class 处理客户端连接和断开连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package com.itcast.netty.chat;import io.netty.channel.Channel;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;import java.util.HashSet;public class ChatConnectionServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { public static HashSet<Channel> onlineUsers = new HashSet <Channel>(); @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("客户端:" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "上线了" ); onlineUsers.add(ctx.channel()); } @Override public void channelInactive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("客户端:" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "断开连接" ); onlineUsers.remove(ctx.channel()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
客户端: ChatClient.class 客户端启动类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 package com.itcast.netty.chat;import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;import java.util.Scanner;public class ChatClient { private final String host; private final int port; public ChatClient (String host, int port) { this .port = port; this .host = host; } public void run () throws InterruptedException { NioEventLoopGroup groups = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { Bootstrap client = new Bootstrap (); client.group(groups); client.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); client.handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new StringDecoder (), new StringEncoder (), new ChatClientHandler () ); } }); ChannelFuture clientChannel = client.connect(host, port).sync(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); while (true ) { String msg = scanner.nextLine(); if ("exit" .equals(msg)) { break ; } clientChannel.channel().writeAndFlush(msg); } clientChannel.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { groups.shutdownGracefully(); } } public static void main (String[] args) { ChatClient client = new ChatClient ("localhost" , 3333 ); try { client.run(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
ChatClientHandler.class 处理服务器发来的消息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package com.itcast.netty.chat;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;public class ChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <String> { @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String msg) throws Exception { System.out.println(msg); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
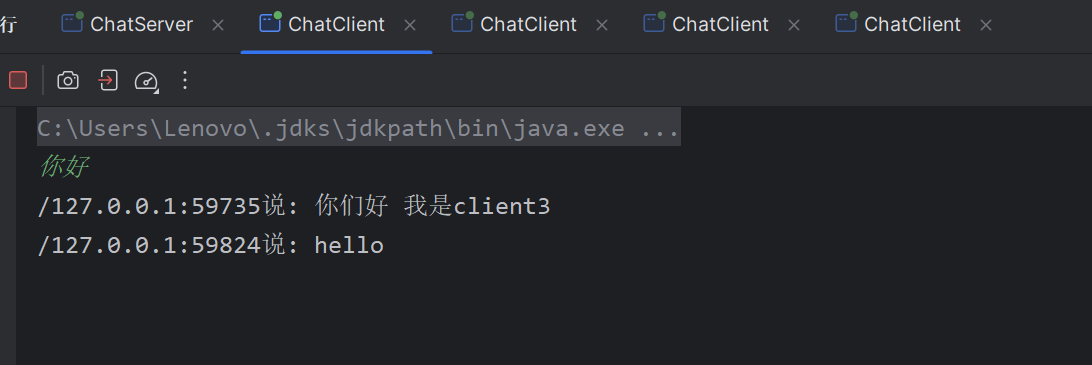
运行结果:
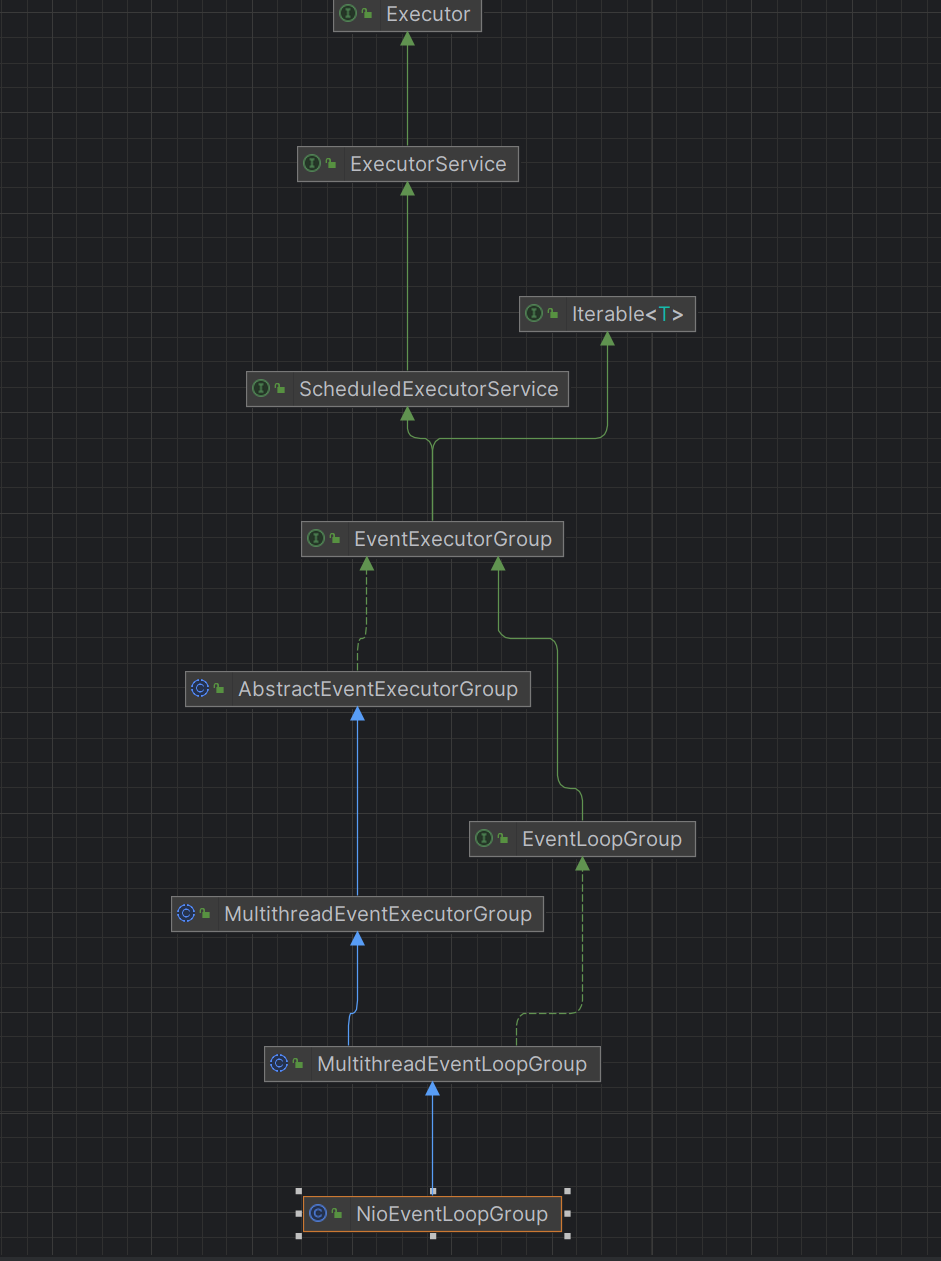
Netty源码剖析 EventLoopGroup 和EventLoop 从EventLoopGroup接口的继承关系图可以从看出来这个接口继承了ExecutorService接口,说明是一个线程池
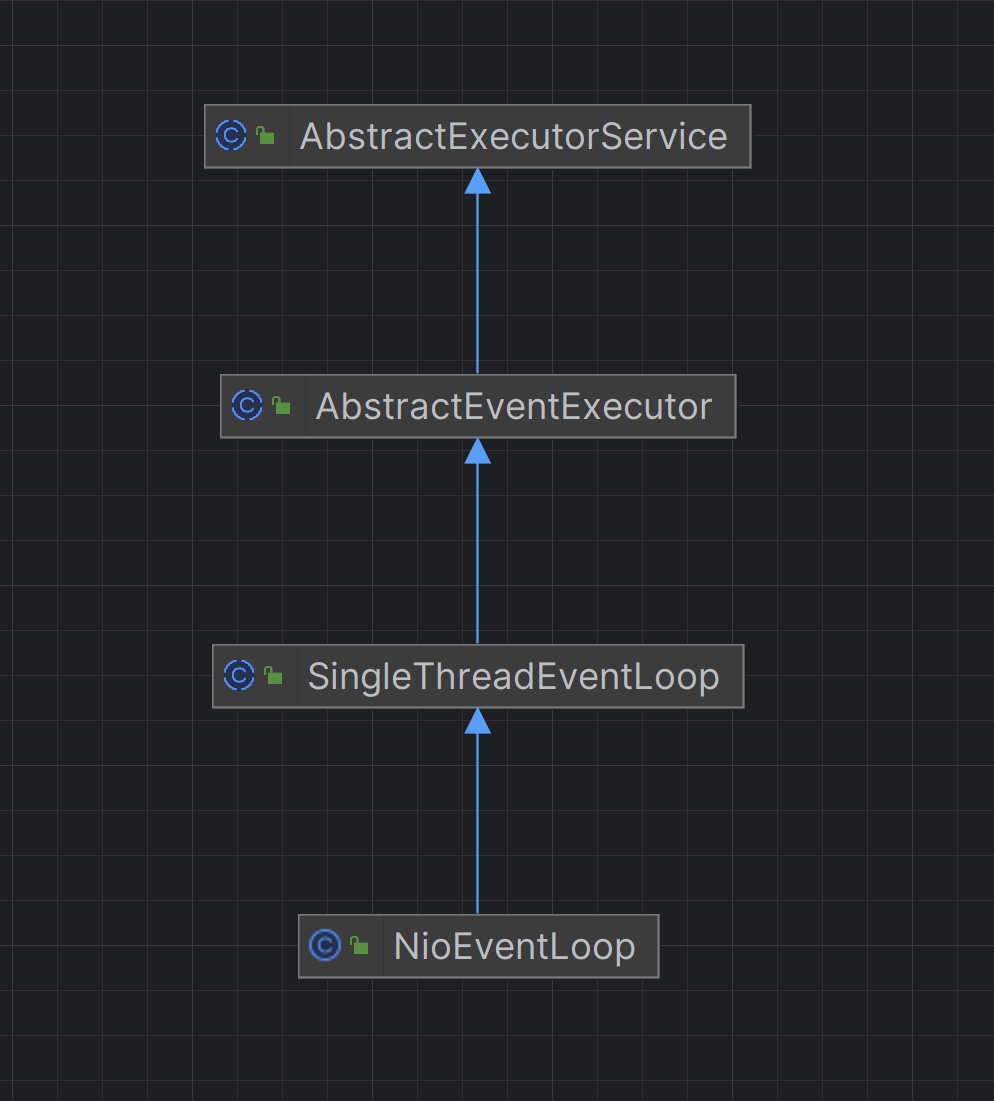
NioEventLoop
处理 I/O 多路复用,监听 Channel 上的事件
NioEventLoop 是 Netty 基于 Java NIO 机制构建的事件循环实现
NioEvent通过组合方式管理线程和任务。
NioEventLoop → SingleThreadEventLoop → SingleThreadEventExecutor → AbstractScheduledEventExecutor。
Netty 采用 单线程模型 处理 Channel:
每个 EventLoop 绑定一个 专属线程 (Thread)。
该线程负责处理该 EventLoop 管理的 所有 Channel 的 IO 操作 (如读、写、连接)。
所有 Channel 操作必须在其关联的 EventLoop 线程中执行,否则会导致线程安全问题。
重要字段
属性分类
关键属性
作用与优化点
Selector 优化
selectedKeys使用数组替代 HashSet,提升选择键处理性能
任务调度
taskQueue、scheduledTaskQueue分离普通任务和定时任务,支持异步执行
线程控制
threadId、wakenUp确保任务在正确线程执行,优化 Selector.wakeup() 调用
时间管理
ioRatio、lastExecutionTime平衡 I/O 操作和任务执行时间,避免任务饥饿
状态管理
state、needsToSelectAgain控制事件循环状态,处理取消的 SelectionKey
1.Selector相关字段 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private Selector selector;private final SelectorProvider provider;private SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeys;private final Selector unwrappedSelector;
2.任务队列相关字段
taskQueue:存储通过 execute() 提交的普通任务。scheduledTaskQueue:存储通过 schedule() 提交的定时任务。
1 2 3 4 5 private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue;private final PriorityQueue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>> scheduledTaskQueue;
实现:
taskQueue 默认使用 MpscUnboundedArrayQueue(多生产者单消费者队列)。scheduledTaskQueue 使用二叉堆实现,按执行时间排序。
3.父级EventLoopGroup 表示当前EventLoop属于哪个EventLoopGroup
1 2 private final NioEventLoopGroup parent;
4.线程相关
确保任务在正确的线程中执行(通过 inEventLoop() 检查)。
控制 Selector 的唤醒机制(避免不必要的 wakeup() 调用)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private volatile int threadId;private final AtomicBoolean wakenUp = new AtomicBoolean ();private volatile int state = ST_NOT_STARTED;private final int maxPendingTasks;private final RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler;
5.事件相关
selectStrategy:决定何时调用 select()、selectNow() 或跳过选择。needsToSelectAgain:标记是否需要重新执行 select()。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private final SelectStrategy selectStrategy;private int cancelledKeys;private boolean needsToSelectAgain;
6. 时间与执行控制属性
ioRatio:控制 I/O 操作与任务执行的时间分配。lastExecutionTime:用于计算任务执行超时和延迟调度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private final int ioRatio;private long lastExecutionTime;private static final long SCHEDULE_PURGE_INTERVAL = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(1 );
线程管理 每个 NioEventLoop 绑定一个独立线程 :
处理注册到Selector上的IO 事件 (连接、读写等)。
执行用户提交的普通任务 (通过execute(task))和定时任务 (通过schedule(task, delay, unit))。
调度后续的任务执行(如定时任务)。
NioEventLoop内部没有线程池,它是一个单线程的事件循环 ,所有操作都在同一个线程中完成。
NioEventLoop会将耗时任务通过NioEventLoopGroup提交到外部的线程池中
重要方法 run方法:
NioEventLoop 通过内部线程执行 run() 方法,通过 execute(Runnable) 提交任务
无限循环处理 I/O 事件和任务队列。
通过 processSelectedKeys() 处理网络 I/O。
通过 runAllTasks() 执行提交的 Runnable 任务。
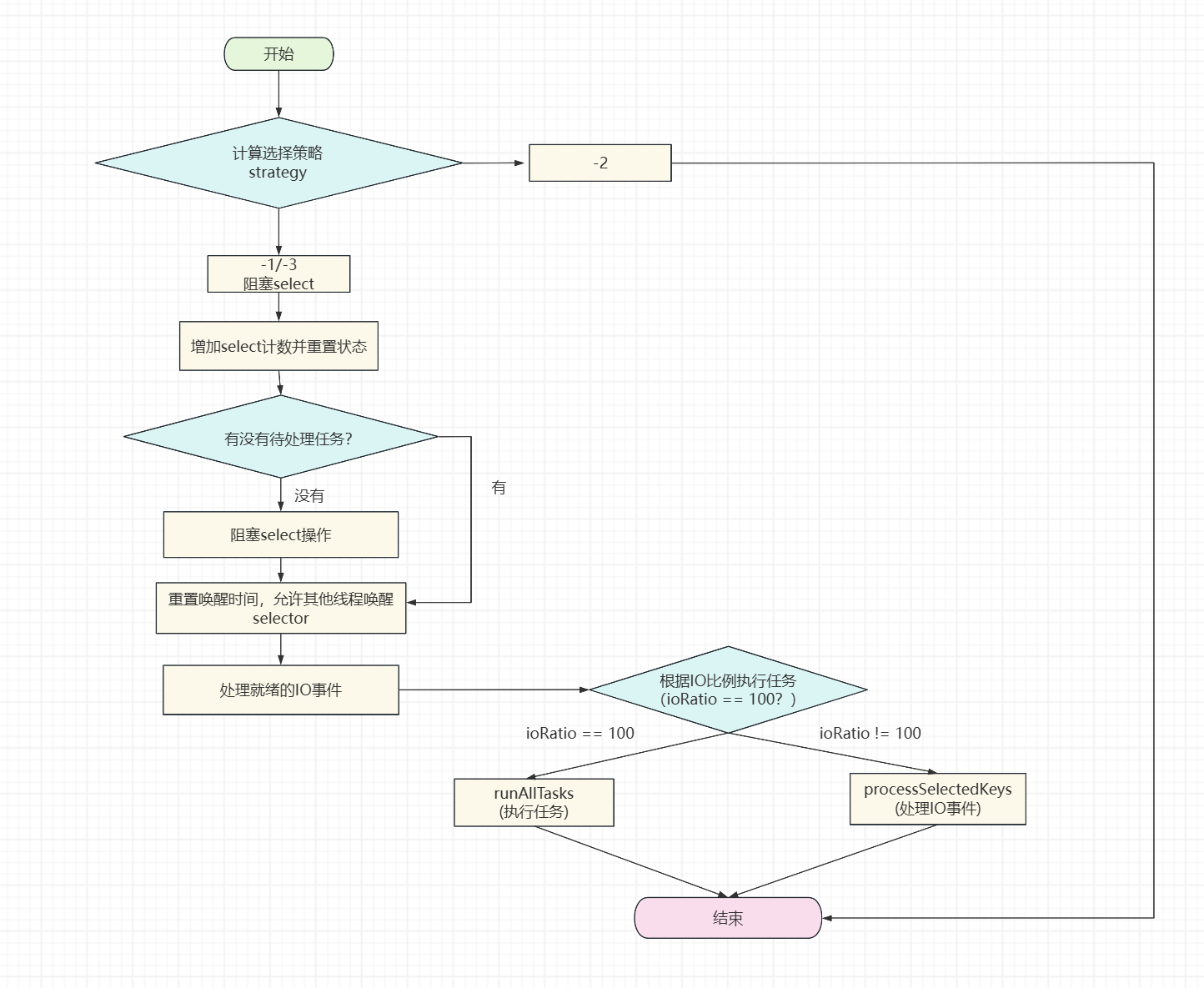
calculateStrategy 是 Netty 中用于决定 EventLoop 选择策略的核心方法,它平衡了 I/O 事件处理与任务执行的优先级。该方法由 SelectStrategy 接口定义,默认实现为 DefaultSelectStrategy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 protected void run () { int selectCnt = 0 ; while (true ) { try { int strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks()); switch (strategy) { case -3 : case -1 : long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos(); if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L ) { curDeadlineNanos = Long.MAX_VALUE; } nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos); try { if (!hasTasks()) { strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos); } } finally { nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(-1L ); } break ; case -2 : break outerLoop; } ++selectCnt; cancelledKeys = 0 ; needsToSelectAgain = false ; int ioRatio = this .ioRatio; boolean ranTasks; if (strategy > 0 ) { processSelectedKeys(); } if (ioRatio == 100 ) { ranTasks = runAllTasks(); } else { long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); try { if (strategy > 0 ) { processSelectedKeys(); } } finally { long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime; ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (long )(100 - ioRatio) / (long )ioRatio); } } if (!ranTasks && strategy <= 0 ) { if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt)) { selectCnt = 0 ; } } if (selectCnt > 3 && logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}." , selectCnt - 1 , selector); } selectCnt = 0 ; } catch (IOException e) { rebuildSelector0(); selectCnt = 0 ; handleLoopException(e); } catch (CancelledKeyException e) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("CancelledKeyException raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?" , selector, e); } } catch (Error e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { handleLoopException(e); } finally { if (isShuttingDown()) { closeAll(); if (confirmShutdown()) { return ; } } } } }
**select(curDeadlineNanos)**:
deadlineNanos:下一个定时任务的截止时间Long.MAX_VALUE 表示无定时任务,可永久阻塞deadlineNanos + 995000L:增加 995000 纳秒(约 1 毫秒)以避免浮点数精度误差 。deadlineToDelayNanos():计算当前时间到 deadlineNanos 的剩余时间(纳秒)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private int select (long deadlineNanos) throws IOException { if (deadlineNanos == Long.MAX_VALUE) { return this .selector.select(); } else { long timeoutMillis = deadlineToDelayNanos(deadlineNanos + 995000L ) / 1000000L ; return timeoutMillis <= 0L ? this .selector.selectNow() : this .selector.select(timeoutMillis); } }
**processSelectedKeys**: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private void processSelectedKeys () { if (this .selectedKeys != null ) { this .processSelectedKeysOptimized(); } else { this .processSelectedKeysPlain(this .selector.selectedKeys()); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 private void processSelectedKeysOptimized () { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .selectedKeys.size; ++i) { SelectionKey k = this .selectedKeys.keys[i]; this .selectedKeys.keys[i] = null ; Object a = k.attachment(); if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) { processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a); } else { NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask) a; processSelectedKey(k, task); } if (this .needsToSelectAgain) { this .selectedKeys.reset(i + 1 ); this .selectAgain(); i = -1 ; } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 private void processSelectedKeysPlain (Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys) { if (!selectedKeys.isEmpty()) { Iterator<SelectionKey> i = selectedKeys.iterator(); while (true ) { SelectionKey k = i.next(); Object a = k.attachment(); i.remove(); if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) { processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a); } else { NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask) a; processSelectedKey(k, task); } if (!i.hasNext()) { break ; } if (this .needsToSelectAgain) { selectAgain(); selectedKeys = this .selector.selectedKeys(); if (selectedKeys.isEmpty()) { break ; } i = selectedKeys.iterator(); } } } }
**runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos)**: Netty 使用**优先级队列(PriorityQueue)**管理定时任务,队列中的任务按执行时间排序。当调用 runAllTasks() 时,会先将**已到期的任务**从定时队列提取到普通任务队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 protected boolean runAllTasks (long timeoutNanos) { this .fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue(); Runnable task = this .pollTask(); if (task == null ) { this .afterRunningAllTasks(); return false ; } long deadline = timeoutNanos > 0L ? this .getCurrentTimeNanos() + timeoutNanos : 0L ; long runTasks = 0L ; long lastExecutionTime; while (true ) { safeExecute(task); ++runTasks; if ((runTasks & 63L ) == 0L ) { lastExecutionTime = this .getCurrentTimeNanos(); if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) { break ; } } task = this .pollTask(); if (task == null ) { lastExecutionTime = this .getCurrentTimeNanos(); break ; } } this .afterRunningAllTasks(); this .lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime; return true ; }
NioEventLoopGroup 参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ZhuChangwu/p/11192219.html
NioEventLoopGroup 是 Netty 框架中处理网络 IO 操作的核心组件,它管理一组 NioEventLoop 实例,负责注册 Channel、处理 IO 事件和执行任务
重要字段 1. 线程池相关字段 1 2 3 private final EventExecutor[] children; private final Set<EventExecutor> readonlyChildren; private final EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser;
children :存储所有 NioEventLoop 实例,负责实际的 IO 操作和任务执行。chooser :负责从 children 中选择一个 EventLoop,实现负载均衡。
2. 线程配置字段 1 2 3 private final int nThreads; private final Executor executor; private final EventExecutorGroup parent;
nThreads :指定线程池大小,默认是 CPU 核心数的两倍(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2)。executor :实际执行任务的线程池,默认使用 ThreadPerTaskExecutor。
3. Selector 配置字段 1 2 private final SelectorProvider provider; private final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory;
provider :创建 JDK NIO Selector 的工厂,默认使用系统默认实现。selectStrategyFactory :创建选择策略,控制 EventLoop 的 select 行为。
4. 拒绝策略和任务队列字段 1 2 private final RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler; private final EventLoopTaskQueueFactory taskQueueFactory;
rejectedExecutionHandler :当任务队列已满时的拒绝策略,默认使用 AbortPolicy。
重要方法 1. 构造方法 1 2 3 4 public NioEventLoopGroup () public NioEventLoopGroup (int nThreads) public NioEventLoopGroup (int nThreads, Executor executor) public NioEventLoopGroup (int nThreads, Executor executor, SelectorProvider provider)
初始化 EventLoopGroup,指定线程数、执行器和 Selector 提供者等参数。
2. 线程选择方法 1 public EventExecutor next ()
从 children 数组中选择一个 EventLoop,通过 chooser 实现负载均衡。
3. Channel 注册方法 1 public ChannelFuture register (Channel channel)
将 Channel 注册到一个 EventLoop 的 Selector 上,返回异步注册结果。
4. 优雅关闭方法 1 2 public Future<?> shutdownGracefully()public Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
优雅关闭线程池,允许在指定时间内完成未执行的任务。
5. 任务提交方法 1 2 public <T> Future<T> submit (Callable<T> task) public Future<?> execute(Runnable task)
向 EventLoop 提交任务,由线程池异步执行。
6. 资源清理方法 1 protected void cleanup ()
清理资源,关闭所有 EventLoop 和 Selector。
工作流程
初始化阶段 :
创建并启动指定数量的 NioEventLoop 线程。
初始化线程选择器 chooser,用于负载均衡。
Channel 注册阶段 :
调用 register(Channel) 方法将 Channel 注册到一个 EventLoop。
EventLoop 将 Channel 注册到其管理的 Selector 上。
IO 事件处理阶段 :
EventLoop 不断循环调用 Selector.select() 方法检测就绪事件。
处理就绪的 IO 事件(读 / 写),并执行相应的 ChannelHandler。
任务执行阶段 :
通过 execute() 或 submit() 方法提交的任务在 EventLoop 线程中执行。
定时任务由 ScheduledExecutorService 管理和执行。
关闭阶段 :
调用 shutdownGracefully() 方法优雅关闭线程池。
释放所有资源,包括 Selector 和线程。
初始化逻辑
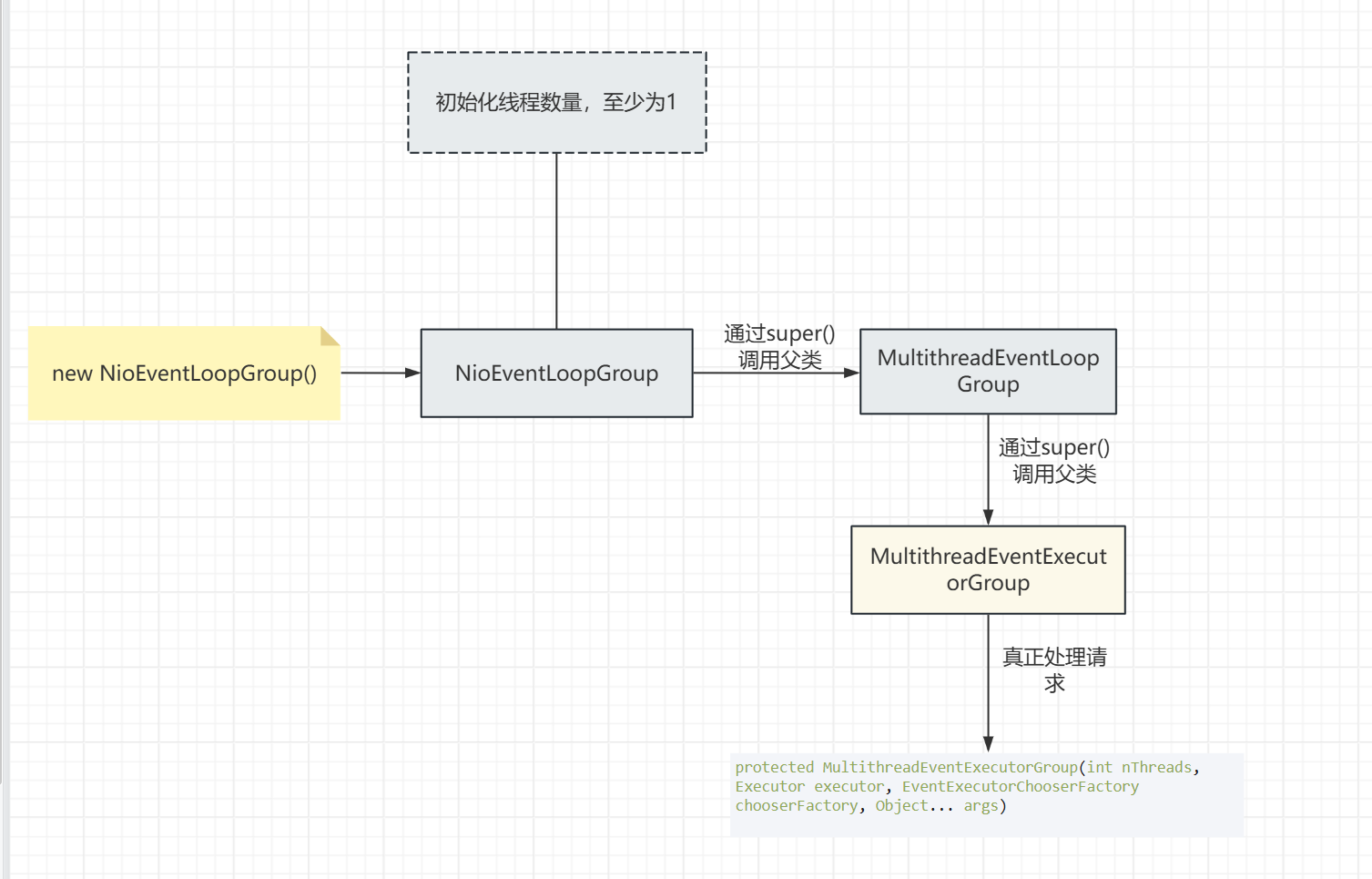
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup (int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) { this .terminatedChildren = new AtomicInteger (); this .terminationFuture = new DefaultPromise (GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE); ObjectUtil.checkPositive(nThreads, "nThreads" ); if (executor == null ) { executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor (this .newDefaultThreadFactory()); } this .children = new EventExecutor [nThreads]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nThreads; ++i) { boolean success = false ; boolean inTryBlock = false ; try { inTryBlock = true ; this .children[i] = this .newChild((Executor)executor, args); success = true ; inTryBlock = false ; } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalStateException ("failed to create a child event loop" , e); } finally { if (inTryBlock && !success) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; ++j) { this .children[j].shutdownGracefully(); } for (int j = 0 ; j < i; ++j) { EventExecutor e = this .children[j]; try { while (!e.isTerminated()) { e.awaitTermination(2147483647L , TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } catch (InterruptedException ie) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); break ; } } } } if (!success) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; ++j) { this .children[j].shutdownGracefully(); } for (int j = 0 ; j < i; ++j) { EventExecutor e = this .children[j]; try { while (!e.isTerminated()) { e.awaitTermination(2147483647L , TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } catch (InterruptedException ie) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); break ; } } } } this .chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(this .children); FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener <Object>() { public void operationComplete (Future<Object> future) throws Exception { if (MultithreadEventExecutorGroup.this .terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == MultithreadEventExecutorGroup.this .children.length) { MultithreadEventExecutorGroup.this .terminationFuture.setSuccess((Object)null ); } } }; EventExecutor[] executors = this .children; for (int i = 0 ; i < executors.length; ++i) { EventExecutor e = executors[i]; e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener); } Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet (this .children.length); Collections.addAll(childrenSet, this .children); this .readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet); }
这个方法主要是:
1.初始化EventLoop数组 根据传递进来的线程数,创建EventLoop,将EventLoop存储在一个EventExecutor[]数组(即children)中
1 this .children[i] = this .newChild((Executor)executor, args);
这个newChild方法调用的是MultithreadEventExecutorGroup里面的newChild方法返回的是一个EventExecutor,EventLoop接口继承了EventExecutor,所以这个EventExecutor其实是一个EventLoop对象
3 .初始化选择器chooser :这个chooser是一个EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser对象,这个对象提供了一个next方法,返回的是EventExecutor对象,所以这个选择器用于从EventLoopGroup中选取一个EventLoop
1 this .chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(this .children);
核心逻辑 当NioEventLoopGroup接收客户端的连接时,会先分配一个NioEventLoop给当前的客户端,当前这个线程池会将客户端channel传递给NioEventLoop,这个NioEventLoop会将调用SingleThreadEventLoop的register方法将当前的客户端注册到当前的NIOEventLoop中
SingleThreadEventLoop.register:
参数检查 :确保 promise 不为空。
获取 Unsafe 对象 : promise.channel().unsafe()
获取 Channel 的内部 Unsafe 实现。
Unsafe :是 Netty 内部使用的接口,提供了底层操作的能力,如注册、绑定、读写等。
调用 Unsafe.register ()
将当前 NioEventLoopGroup 中的一个 EventLoop(通过 next() 方法选择)传递给 Unsafe。
Unsafe 实现会负责实际的注册操作。
返回 Promise :返回原始的 promise 对象,用于异步获取注册结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public ChannelFuture register (ChannelPromise promise) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise" ); promise.channel().unsafe().register(this , promise); return promise; }
然后这个方法最终会调用AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe.register(处理具体的注册逻辑)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 public final void register (EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(eventLoop, "eventLoop" ); if (AbstractChannel.this .isRegistered()) { promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException ("registered to an event loop already" )); return ; } if (!AbstractChannel.this .isCompatible(eventLoop)) { promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException ( "incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName())); return ; } AbstractChannel.this .eventLoop = eventLoop; if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) { register0(promise); } else { try { eventLoop.execute(new Runnable () { @Override public void run () { register0(promise); } }); } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}" , AbstractChannel.this , t); closeForcibly(); AbstractChannel.this .closeFuture.setClosed(); safeSetFailure(promise, t); } } } private void register0 (ChannelPromise promise) { try { boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered; doRegister(); neverRegistered = false ; registered = true ; pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded(); safeSetSuccess(promise); pipeline.fireChannelRegistered(); if (isActive()) { if (firstRegistration) { pipeline.fireChannelActive(); } else if (config().isAutoRead()) { beginRead(); } } } catch (Throwable t) { closeForcibly(); closeFuture.setClosed(); safeSetFailure(promise, t); } }
假设 :
EventLoop 绑定的线程是 Thread-1。主线程(main)调用 channel.register()。
执行流程 :
主线程进入 register() 方法。
检查当前线程(main)是否是 EventLoop 线程(Thread-1),发现不是。
将 register0() 封装成任务,提交到 EventLoop 的任务队列。
Thread-1 从队列中取出任务并执行 register0()。
注册完成后会触发pipeline.fireChannelActive();会调用AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelActive
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 static void invokeChannelActive (final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next) { EventExecutor executor = next.executor(); if (executor.inEventLoop()) { next.invokeChannelActive(); } else { executor.execute(new Runnable () { public void run () { next.invokeChannelActive(); } }); } } private void invokeChannelActive () { if (this .invokeHandler()) { try { ChannelHandler handler = this .handler(); DefaultChannelPipeline.HeadContext headContext = this .pipeline.head; if (handler == headContext) { headContext.channelActive(this ); } else if (handler instanceof ChannelDuplexHandler) { ((ChannelDuplexHandler)handler).channelActive(this ); } else { ((ChannelInboundHandler)handler).channelActive(this ); } } catch (Throwable var3) { this .invokeExceptionCaught(var3); } } else { this .fireChannelActive(); } }
头部处理器:
是Netty 底层 I/O 操作的入口和出口,负责处理与物理通道(如 TCP 连接)直接相关的操作,并衔接上层业务处理器、、
AbstractChannel AbstractChannel 是 Netty 框架中的一个抽象类,它在 Netty 的网络通信中扮演着非常重要的角色,是所有具体通道实现类的基类
AbstractChannel 类是 Netty 框架中实现网络通信的基础,它提供了通道的基本抽象和功能,为上层应用提供了一个统一的、高效的网络编程接口。通过继承 AbstractChannel,Netty 实现了多种不同类型的通道(如 NioServerSocketChannel、NioSocketChannel 等
属性字段
字段名称 类型 核心作用 设计要点 / 场景
parentChannel父通道引用(如服务器通道对应的客户端通道)
用于层级管理,父通道关闭时可级联关闭子通道
idChannelId通道全局唯一标识符
基于 UUID 生成,用于日志、监控标识特定连接
unsafeChannel.Unsafe底层传输操作接口(如 Java NIO 的 Selector 操作)
解耦 Netty 抽象层与具体 IO 模型(NIO/Epoll),提供 read()、write() 等底层方法
pipelineDefaultChannelPipeline处理器链(ChannelHandler 链表)
处理入站 / 出站事件,支持动态添加 / 删除处理器,实现业务逻辑与 IO 的解耦
closeFutureCloseFuture通道关闭事件的异步通知机制
基于 Future-Listener 模式,支持非阻塞式关闭回调(如资源释放)
eventLoopEventLoop关联的事件循环线程(NioEventLoop 等)
通道的所有 IO 操作必须在此线程执行,确保线程安全
registeredboolean标识通道是否已注册到 Selector
true 表示可开始监听 IO 事件(如 OP_READ),由 register() 方法更新
localAddressSocketAddress本地绑定地址(如服务器端口)
绑定端口后设置(如 0.0.0.0:8080)
remoteAddressSocketAddress远程连接地址(如客户端 IP + 端口)
客户端连接建立后设置(如 192.168.1.1:50000)
unsafeVoidPromiseVoidChannelPromise空操作的 ChannelPromise(占位符)
用于不需要返回结果的操作(如内部清理),避免创建临时对象
closeInitiatedboolean标识是否已发起关闭流程
防止重复关闭,确保关闭逻辑幂等性
initialCloseCauseThrowable关闭原因(异常信息)
方法
方法名称 参数 返回值 核心功能 设计要点 / 典型场景
register(EventLoop, Promise)EventLoop, ChannelPromisevoid将通道注册到指定 EventLoop 的 Selector 上
线程安全设计:若当前线程不是 EventLoop 线程,通过 execute() 提交任务确保单线程执行
bind(SocketAddress, Promise)SocketAddress, ChannelPromiseChannelFuture绑定本地地址(如服务器端口)
异步操作:返回 ChannelFuture 监听绑定结果,内部调用 doBind() 实现具体逻辑
connect(SocketAddress, Promise)SocketAddress, ChannelPromiseChannelFuture连接远程地址(客户端模式)
异步操作:支持超时设置,内部调用 doConnect() 实现具体连接逻辑
disconnect(Promise)ChannelPromiseChannelFuture断开连接(客户端模式)
通常用于主动关闭连接,释放资源,内部调用 doDisconnect()
close(Promise)ChannelPromiseChannelFuture关闭通道(优雅关闭)
触发 pipeline 的 channelInactive() 事件,确保所有处理器有机会执行清理逻辑
write(Object, Promise)Object(消息), ChannelPromiseChannelFuture将消息写入通道(异步操作)
消息从 pipeline 的尾部开始流动,最终调用 unsafe.write() 执行底层写操作
flush()voidChannel强制刷新缓冲区,将数据发送到网络
通常与 write() 配合使用(如 writeAndFlush()),触发 pipeline 的 flush() 事件
read()voidChannel触发通道读取数据(从网络接收数据)
调用 pipeline 的 read() 事件,最终调用 unsafe.beginRead() 注册 OP_READ 事件
pipeline()voidChannelPipeline获取通道的 ChannelPipeline(处理器链)
线程安全:每个通道有独立的 pipeline,支持动态添加 / 删除处理器
config()voidChannelConfig获取通道配置(如 TCP_NODELAY、SO_KEEPALIVE 等)
配置参数通过 ChannelOption 设置,影响底层 Socket 行为
localAddress()voidSocketAddress获取本地绑定地址
绑定后返回 localAddress 字段值,否则返回 null
remoteAddress()voidSocketAddress获取远程连接地址
连接建立后返回 remoteAddress 字段值,否则返回 null
isActive()voidboolean判断通道是否处于活跃状态(已连接或已绑定)
通常用于检查通道是否可进行读写操作
Netty服务器启动源码剖析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap ();server.group(bossGroup, workGroups); server.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); server.handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioServerSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioServerSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.INFO)); } }); ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> childHandlers = new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new StringDecoder (), new StringEncoder (), new ChatServerHandler (), new ChatConnectionServerHandler () ); } }; server.childHandler(childHandlers); server.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ); ChannelFuture serverChannel = server.bind(port).sync();serverChannel.channel().closeFuture().sync();
**创建并初始化 ServerSocketChannel**:
ServerBootstrap 根据配置创建一个 ServerSocketChannel,用于监听客户端连接。配置 ServerSocketChannel 的一些参数,如 SO_BACKLOG(连接队列长度)等。
**将 ServerSocketChannel 注册到 EventLoop**:
ServerSocketChannel 会被注册到 EventLoop 的 Selector 上,以便监听连接事件。注册过程是异步的,通过 ChannelFuture 来通知注册结果。
绑定端口 :
调用 ServerSocketChannel 的 bind 方法,将其绑定到指定的端口。
底层会调用操作系统的 bind 系统调用,将套接字绑定到指定的 IP 地址和端口。
启动监听 :
绑定成功后,ServerSocketChannel 开始监听客户端连接。
此时,ServerSocketChannel 处于 OP_ACCEPT 状态,等待客户端连接。
阻塞等待绑定完成 :
sync() 方法会阻塞当前线程,直到绑定操作完成。如果绑定成功,ChannelFuture 的 isSuccess() 方法返回 true;如果绑定失败,ChannelFuture 的 isSuccess() 方法返回 false,并且可以通过 cause() 方法获取失败原因。
触发 ChannelActive 事件 :
如果 Channel 在绑定后变为活跃状态(之前不活跃),会异步触发 ChannelActive 事件。
ChannelActive 事件会被传播到 ChannelPipeline 中的所有 ChannelHandler,以便它们可以执行相应的初始化或处理逻辑。
1.初始化EventLoopGroup 1 server.group(bossGroup, workerGroups);
调用ServerBootStrap的group方法指定bossGroup和workerGroup
workerGroup会传递给ServerBootStrap类,指定childGroup为workerGroupbossGroup会传递给AbstractBootstrap这个类,指定这个类的group属性为传递的bossGroup
(ServerBootStrap类继承了AbstractBootstrap类)
一般情况下:
bossGroup可以认为是主Reactor线程池,主要负责处理客户端的连接请求 (accept事件),建立与客户端的连接
workerGroup可以认为是从Reactor线程池。主要负责处理已建立连接的 Channel 的读写事件 (read/write事件),包括数据的接收、处理和发送
2.初始化channel 主要是设置AbstractBootstrap里面的channelFactory属性设置为对应通道类型的工厂类
1 server.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
调用的是父类AbstractBootstrap的channel方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public B channel (Class<? extends C> channelClass) { return this .channelFactory((io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory)(new ReflectiveChannelFactory ((Class)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelClass, "channelClass" )))); } public B channelFactory (io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) { return this .channelFactory((ChannelFactory)channelFactory); } public B channelFactory (ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelFactory, "channelFactory" ); if (this .channelFactory != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("channelFactory set already" ); } else { this .channelFactory = channelFactory; return this .self(); } }
ReflectiveChannelFactory 是 Netty 中用于通过反射创建 Channel 实例 的工厂类
ReflectiveChannelFactory通过channelClass(当前通道的类型)通过反射拿到对应类(当前通道)的无参构造器
ReflectiveChannelFactory实现了ChannelFactory接口,所以它是ChannelFactory的子类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public ReflectiveChannelFactory (Class<? extends T> clazz) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(clazz, "clazz" ); try { this .constructor = clazz.getConstructor(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var3) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Class " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) + " does not have a public non-arg constructor" , var3); } }
通过channelFactory方法将当前类的channelFactory属性初始化为ReflectiveChannelFactory对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public B channelFactory (ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelFactory, "channelFactory" ); if (this .channelFactory != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("channelFactory set already" ); } else { this .channelFactory = channelFactory; return this .self(); } }
ChannelFactory接口提供了一个newChannel方法,这个方法对应的实现类是ReflectiveChannelFactory,这个方法返回通过反射拿到的构造器创建对应通道类型的实例(即NioServerSocketChannel实例)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public T newChannel () { try { return (Channel)this .constructor.newInstance(); } catch (Throwable var2) { throw new ChannelException ("Unable to create Channel from class " + this .constructor.getDeclaringClass(), var2); } }
3.初始化处理器 在 Netty 中,**ChannelInitializer** 是一个核心组件,用于动态初始化 Channel 的处理器链(ChannelPipeline)
会在 Channel 注册到EventLoop后、真正开始处理数据前,动态添加处理器
当 Channel 注册到EventLoop时,ChannelInitializer的initChannel()方法会被触发,会调用AbstractChannel类的pipeline方法给当前Channel的ChannelPipeline对象(即pipeline)添加处理器链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new StringDecoder (), new StringEncoder (), new ChatServerHandler (), new ChatConnectionServerHandler () ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public final ChannelPipeline addLast (EventExecutorGroup executor, ChannelHandler... handlers) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(handlers, "handlers" ); ChannelHandler[] var3 = handlers; int var4 = handlers.length; for (int var5 = 0 ; var5 < var4; ++var5) { ChannelHandler h = var3[var5]; if (h == null ) { break ; } this .addLast(executor, (String)null , h); } return this ; }
初始化主通道处理器(handler()) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 server.handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioServerSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioServerSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.INFO)); } });
调用入口是AbstractBootstrap类的handler方法,将AbstractBootstrap类的handler属性设置为传入的处理器,主要用于处理bossGroup
1 2 3 4 public B handler (ChannelHandler handler) { this .handler = (ChannelHandler)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(handler, "handler" ); return this .self(); }
初始化子通道处理器(childHandler()) 客户端连接服务器时,为客户端通道添加处理器链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> childHandlers = new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new StringDecoder (), new StringEncoder (), new ChatServerHandler (), new ChatConnectionServerHandler () ); } }; server.childHandler(childHandlers);
调用的入口是ServerBootStrap的childHandler方法,主要是将ServerBootStrap的子处理器childHandler设置为传入的处理器
这个子处理器其实就是用于处理workerGroup
1 2 3 4 public ServerBootstrap childHandler (ChannelHandler childHandler) { this .childHandler = (ChannelHandler)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(childHandler, "childHandler" ); return this ; }
4.绑定端口并启动服务 1 2 ChannelFuture serverChannel = server.bind(port).sync();
调用关系图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. ServerBootstrap.bind(port) 2. -> AbstractBootstrap.doBind(localAddress) 3. -> Channel.bind(localAddress) 4. -> ChannelPipeline.bind() 5. -> HeadContext.bind() 6. -> NioMessageUnsafe.bind() 7. -> ServerSocketChannel.bind() 8. -> OS socket.bind() 9. -> OS socket.listen() 10. serverChannel.sync()
入口函数:调用AbstractBootstrap的bind方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public ChannelFuture bind (int inetPort) { return this .bind(new InetSocketAddress (inetPort)); } public ChannelFuture bind (SocketAddress localAddress) { this .validate(); return this .doBind((SocketAddress)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress" )); } private ChannelFuture doBind (final SocketAddress localAddress) { final ChannelFuture regFuture = this .initAndRegister(); final Channel channel = regFuture.channel(); if (regFuture.cause() != null ) { return regFuture; } else if (regFuture.isDone()) { ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise(); doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); return promise; } else { final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise (channel); regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener () { public void operationComplete (ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { Throwable cause = future.cause(); if (cause != null ) { promise.setFailure(cause); } else { promise.registered(); AbstractBootstrap.doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); } } }); return promise; } }
4.1.初始化并注册Channel 调用AbstractBootstrap的initAndRegister方法
1.通过channelFactory工厂类,创建通道实例channel
2.通过this.init(channel)初始化当前通道,负责初始化服务器 Channel 的各项参数和处理器链。
3.将 Channel 注册到 EventLoopGroup 中的某个 EventLoop
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 final ChannelFuture initAndRegister () { Channel channel = null ; try { channel = this .channelFactory.newChannel(); this .init(channel); } catch (Throwable t) { if (channel != null ) { channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); return new DefaultChannelPromise (channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t); } return new DefaultChannelPromise (new FailedChannel (), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t); } ChannelFuture regFuture = this .config().group().register(channel); if (regFuture.cause() != null ) { if (channel.isRegistered()) { channel.close(); } else { channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); } } return regFuture; }
1.通过channelFactory属性创建对应通道类型的实例(channelFactory这个工厂类是在初始化的时候创建的)
1 channel = this .channelFactory.newChannel();
2.通过调用ServerBootstrap类的init方法初始化当前通道
2.1.配置服务器 Channel :设置选项(如 SO_BACKLOG)和属性。
2.2.构建 Pipeline :添加主处理器(如 LoggingHandler)和 ServerBootstrapAcceptor。
2.3.处理新连接 :
ServerBootstrapAcceptor 负责创建子 Channel(SocketChannel)。为子 Channel 配置处理器链(如 HttpServerCodec)。
将子 Channel 注册到 childGroup 的 EventLoop。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 void init (Channel channel) { setChannelOptions(channel, this .newOptionsArray(), logger); setAttributes(channel, this .newAttributesArray()); ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = this .childGroup; final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = this .childHandler; p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer <Channel>() { @Override public void initChannel (final Channel ch) { ChannelHandler handler = ServerBootstrap.this .config.handler(); if (handler != null ) { pipeline.addLast(handler); } ch.eventLoop().execute(() -> { pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor ( ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs, extensions )); }); } }); if (!extensions.isEmpty() && channel instanceof ServerChannel) { } }
ServerBootstrapAcceptor 是一个特殊的 ChannelInboundHandler,它作为连接管理器 存在于 NioServerSocketChannel 的 Pipeline 中,主要负责:
接收新连接 :当主 Reactor(bossGroup)检测到客户端连接请求时,创建对应的 NioSocketChannel。分配 EventLoop :从从 Reactor(childGroup)中选择一个 EventLoop 分配给新连接。初始化子 Channel :为新连接的 NioSocketChannel 配置处理器链(Pipeline)和选项。注册到 Selector :将新连接注册到分配的 EventLoop 的 Selector 上,开始监听读写事件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ch.eventLoop().execute(() -> { pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor ( ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs, extensions )); });
当有新客户端连接时,ServerBootstrapAcceptor 的 channelRead() 方法会被触发
核心功能:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { final Channel child = (Channel) msg; child.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelHandler []{this .childHandler}); AbstractBootstrap.setChannelOptions(child, this .childOptions, ServerBootstrap.logger); AbstractBootstrap.setAttributes(child, this .childAttrs); if (!this .extensions.isEmpty()) { Iterator var4 = this .extensions.iterator(); while (var4.hasNext()) { ChannelInitializerExtension extension = (ChannelInitializerExtension)var4.next(); try { extension.postInitializeServerChildChannel(child); } catch (Exception var8) { ServerBootstrap.logger.warn("Exception thrown from postInitializeServerChildChannel" , var8); } } } try { this .childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener () { public void operationComplete (ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (!future.isSuccess()) { ServerBootstrap.ServerBootstrapAcceptor.forceClose(child, future.cause()); } } }); } catch (Throwable var7) { forceClose(child, var7); } }
3. 将 Channel 注册到 EventLoopGroup 中的某个 EventLoop :
1 ChannelFuture regFuture = this .config().group().register(channel);
是 Netty 服务器启动流程中的核心操作,负责将 Channel 注册到 EventLoop 的 Selector ,从而建立事件循环机制。这个操作标志着 Channel 开始真正参与网络 IO 处理。
ChannelFuture封装异步操作结果 :
立即返回 :调用 register(channel) 后,方法会立即返回一个 ChannelFuture,此时注册操作可能尚未完成。异步完成 :Netty 会在后台完成实际的注册操作,完成后通过 ChannelFuture 通知结果。
config().group()
**config()**:返回 AbstractBootstrapConfig,包含启动配置信息。
**group()**:返回EventLoopGroup(线程池):
**对于 ServerBootstrap**:config().group() 返回 **bossGroup**,负责接受客户端连接。ServerBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)。
对于 Bootstrap(客户端) :config().group() 返回唯一的 EventLoopGroup,负责处理所有连接的 IO。
这个register方法最终会调用AbstractChannel类的register方法(AbstractChannel类是所有具体通道实现类的基类,定义了通道的一些通用属性和方法),返回一个ChannelFuture对象,
SingleThreadEventLoop.class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public ChannelFuture register (Channel channel) { return this .register((ChannelPromise)(new DefaultChannelPromise (channel, this ))); } public ChannelFuture register (ChannelPromise promise) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise" ); promise.channel().unsafe().register(this , promise); return promise; }
AbstractChannel.class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 public final void register (EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(eventLoop, "eventLoop" ); if (AbstractChannel.this .isRegistered()) { promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException ("Channel 已注册到 EventLoop" )); return ; } if (!AbstractChannel.this .isCompatible(eventLoop)) { promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException ( "不兼容的 EventLoop 类型: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName())); return ; } AbstractChannel.this .eventLoop = eventLoop; if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) { register0(promise); } else { try { eventLoop.execute(() -> register0(promise)); } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("注册任务被 EventLoop 拒绝,强制关闭 Channel: {}" , AbstractChannel.this , t); closeForcibly(); AbstractChannel.this .closeFuture.setClosed(); safeSetFailure(promise, t); } } } private void register0 (ChannelPromise promise) { try { if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) { return ; } boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered; AbstractChannel.this .doRegister(); neverRegistered = false ; registered = true ; pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded(); safeSetSuccess(promise); pipeline.fireChannelRegistered(); if (isActive()) { if (firstRegistration) { pipeline.fireChannelActive(); } else if (config().isAutoRead()) { beginRead(); } } } catch (Throwable t) { closeForcibly(); closeFuture.setClosed(); safeSetFailure(promise, t); } }
4.2 根据注册结果处理绑定 1 2 3 ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); return promise;
调用AbstractBootstrap类的doBind0()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private static void doBind0 ( final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) { channel.eventLoop().execute(() -> { if (regFuture.isSuccess()) { channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } else { promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause()); } }); }
channel.bind会去调用AbstractChannel的pipeline对象,并执行对应的bind方法
1 2 3 public ChannelFuture bind (SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) { return this .pipeline.bind(localAddress, promise); }
执行DefaultChannelPipeline类的bind方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public final ChannelFuture bind (SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) { return this .tail.bind(localAddress, promise); } public final ChannelFuture bind (SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) { return this .tail.bind(localAddress, promise); }
tail是AbstractChannelHandlerContext对象,会调用AbstractChannelHandlerContext类的bind方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 public ChannelFuture bind (final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress" ); if (this .isNotValidPromise(promise, false )) { return promise; } final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = this .findContextOutbound(512 ); EventExecutor executor = next.executor(); if (executor.inEventLoop()) { next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise); } else { safeExecute(executor, () -> next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise), promise, null , false ); } return promise; } private void invokeBind (SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) { if (this .invokeHandler()) { try { ChannelHandler handler = this .handler(); DefaultChannelPipeline.HeadContext headContext = this .pipeline.head; if (handler == headContext) { headContext.bind(this , localAddress, promise); } else if (handler instanceof ChannelDuplexHandler) { ((ChannelDuplexHandler)handler).bind(this , localAddress, promise); } else if (handler instanceof ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter) { ((ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter)handler).bind(this , localAddress, promise); } else { ((ChannelOutboundHandler)handler).bind(this , localAddress, promise); } } catch (Throwable t) { notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise); } } else { this .bind(localAddress, promise); } }
根据handler的类型调用不同的bind方法
以headContext为例:
headContext这个bind方法会调用AbstractChannel的bind方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public final void bind (SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) { this .assertEventLoop(); if (promise.setUncancellable() && this .ensureOpen(promise)) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(AbstractChannel.this .config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) && localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress && !((InetSocketAddress)localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() && !PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) { logger.warn("非 root 用户绑定非通配地址({})可能无法接收广播包,但仍按请求继续绑定" , localAddress); } boolean wasActive = AbstractChannel.this .isActive(); try { AbstractChannel.this .doBind(localAddress); } catch (Throwable t) { this .safeSetFailure(promise, t); this .closeIfClosed(); return ; } if (!wasActive && AbstractChannel.this .isActive()) { this .invokeLater(() -> AbstractChannel.this .pipeline.fireChannelActive()); } this .safeSetSuccess(promise); } } protected abstract void doBind (SocketAddress var1) throws Exception;
调用ServerSocketChannel的doBind方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @SuppressJava6Requirement( reason = "Usage guarded by java version check" ) protected void doBind (SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception { if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7 ) { this .javaChannel().bind(localAddress, this .config.getBacklog()); } else { this .javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, this .config.getBacklog()); } } public abstract ServerSocketChannel bind (SocketAddress local, int backlog) throws IOException;
上面的bind方法会调用ServerSocketChannelImpl的具体实现方法bind
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public ServerSocketChannel bind (SocketAddress local, int backlog) throws IOException { synchronized (this .lock) { if (!this .isOpen()) { throw new ClosedChannelException (); } else if (this .isBound()) { throw new AlreadyBoundException (); } InetSocketAddress addr = local == null ? new InetSocketAddress (0 ) : Net.checkAddress(local); SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null ) { sm.checkListen(addr.getPort()); } NetHooks.beforeTcpBind(this .fd, addr.getAddress(), addr.getPort()); try { Net.bind(this .fd, addr.getAddress(), addr.getPort()); Net.listen(this .fd, backlog < 1 ? 50 : backlog); } catch (IOException e) { try { this .fd.close(); } catch (IOException suppressed) { e.addSuppressed(suppressed); } throw e; } synchronized (this .stateLock) { this .localAddress = Net.localAddress(this .fd); } return this ; } }